Regulation of Hippo signalling by p38 signalling
- PMID: 27402810
- PMCID: PMC4991669
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjw036
Regulation of Hippo signalling by p38 signalling
Abstract
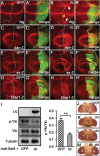
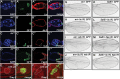
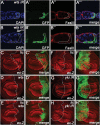
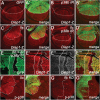
The Hippo signalling pathway has a crucial role in growth control during development, and its dysregulation contributes to tumorigenesis. Recent studies uncover multiple upstream regulatory inputs into Hippo signalling, which affects phosphorylation of the transcriptional coactivator Yki/YAP/TAZ by Wts/Lats. Here we identify the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway as a new upstream branch of the Hippo pathway. In Drosophila, overexpression of MAPKK gene licorne (lic), or MAPKKK gene Mekk1, promotes Yki activity and induces Hippo target gene expression. Loss-of-function studies show that lic regulates Hippo signalling in ovary follicle cells and in the wing disc. Epistasis analysis indicates that Mekk1 and lic affect Hippo signalling via p38b and wts We further demonstrate that the Mekk1-Lic-p38b cascade inhibits Hippo signalling by promoting F-actin accumulation and Jub phosphorylation. In addition, p38 signalling modulates actin filaments and Hippo signalling in parallel to small GTPases Ras, Rac1, and Rho1. Lastly, we show that p38 signalling regulates Hippo signalling in mammalian cell lines. The Lic homologue MKK3 promotes nuclear localization of YAP via the actin cytoskeleton. Upregulation or downregulation of the p38 pathway regulates YAP-mediated transcription. Our work thus reveals a conserved crosstalk between the p38 MAPK pathway and the Hippo pathway in growth regulation.
Keywords: F-actin; Hippo signalling; p38 signalling.
© The Author (2016). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, IBCB, SIBS, CAS.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Hippo pathway integrates PI3K-Akt signals with mechanical and polarity cues to control tissue growth.PLoS Biol. 2019 Oct 15;17(10):e3000509. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000509. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2019. PMID: 31613895 Free PMC article.
-
Ajuba family proteins link JNK to Hippo signaling.Sci Signal. 2013 Sep 10;6(292):ra81. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004324. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 24023255 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Hippo signaling promotes Rho1-JNK-dependent growth.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 27;112(4):1065-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1415020112. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25583514 Free PMC article.
-
The hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer.Dev Cell. 2010 Oct 19;19(4):491-505. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.09.011. Dev Cell. 2010. PMID: 20951342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hippo-YAP pathway: new connections between regulation of organ size and cancer.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008 Dec;20(6):638-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.10.001. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18955139 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of osteoblast behaviors via cross-talk between Hippo/YAP and MAPK signaling pathway under fluoride exposure.J Mol Med (Berl). 2019 Jul;97(7):1003-1017. doi: 10.1007/s00109-019-01785-x. Epub 2019 May 4. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019. PMID: 31055605
-
Role of MAPK/JNK signaling pathway on the regulation of biological behaviors of MC3T3‑E1 osteoblasts under titanium ion exposure.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Dec;22(6):4792-4800. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11575. Epub 2020 Oct 11. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 33173964 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of WW domain-containing oxidoreductase leads to tamoxifen-resistance by the inactivation of Hippo signaling.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2019 Sep;244(12):972-982. doi: 10.1177/1535370219854678. Epub 2019 Jun 2. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2019. PMID: 31155927 Free PMC article.
-
Lic regulates JNK-mediated cell death in Drosophila.Cell Prolif. 2019 May;52(3):e12593. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12593. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Cell Prolif. 2019. PMID: 30847993 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Mediated F-Actin in the Acupuncture-Induced Mitigation of Inflammatory Pain in Arthritic Rats.Brain Sci. 2024 Apr 14;14(4):380. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14040380. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38672029 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumgartner R., Poernbacher I., Buser N., et al. (2010). The WW domain protein Kibra acts upstream of Hippo in Drosophila. Dev. Cell 18, 309–316. - PubMed
-
- Chen H.J., Wang C.M., Wang T.W., et al. (2011). The Hippo pathway controls polar cell fate through Notch signaling during Drosophila oogenesis. Dev. Biol. 357, 370–379. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

