Reversal of Ethanol-induced Intoxication by a Novel Modulator of Gβγ Protein Potentiation of the Glycine Receptor
- PMID: 27402845
- PMCID: PMC5009253
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.740555
Reversal of Ethanol-induced Intoxication by a Novel Modulator of Gβγ Protein Potentiation of the Glycine Receptor
Abstract
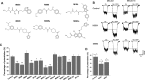
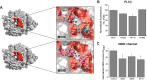
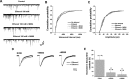
The acute intoxicating effects of ethanol in the central nervous system result from the modulation of several molecular targets. It is widely accepted that ethanol enhances the activity of the glycine receptor (GlyR), thus enhancing inhibitory neurotransmission, leading to motor effects, sedation, and respiratory depression. We previously reported that small peptides interfered with the binding of Gβγ to the GlyR and consequently inhibited the ethanol-induced potentiation of the receptor. Now, using virtual screening, we identified a subset of small molecules capable of interacting with the binding site of Gβγ. One of these compounds, M554, inhibited the ethanol potentiation of the GlyR in both evoked currents and synaptic transmission in vitro When this compound was tested in vivo in mice treated with ethanol (1-3.5 g/kg), it was found to induce a faster recovery of motor incoordination in rotarod experiments and a shorter sedative effect in loss of righting reflex assays. This study describes a novel molecule that might be relevant for the design of useful therapeutic compounds in the treatment of acute alcohol intoxication.
Keywords: G protein; Gβγ; alcohol; glycine receptor; molecular pharmacology; small molecule.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Aguayo L. G., and Pancetti F. C. (1994) Ethanol modulation of the γ-aminobutyric acidA- and glycine-activated Cl− current in cultured mouse neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 270, 61–69 - PubMed
-
- Aguayo L. G., Tapia J. C., and Pancetti F. C. (1996) Potentiation of the glycine-activated Cl− current by ethanol in cultured mouse spinal neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 279, 1116–1122 - PubMed
-
- Zhu L., and Ye J. H. (2005) The role of G proteins in the activity and ethanol modulation of glycine-induced currents in rat neurons freshly isolated from the ventral tegmental area. Brain Res. 1033, 102–108 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

