A Citrus bergamia Extract Decreases Adipogenesis and Increases Lipolysis by Modulating PPAR Levels in Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Human Adipose Tissue
- PMID: 27403151
- PMCID: PMC4926019
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/4563815
A Citrus bergamia Extract Decreases Adipogenesis and Increases Lipolysis by Modulating PPAR Levels in Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Human Adipose Tissue
Abstract
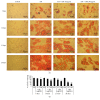
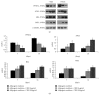
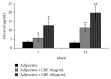
The aim of this research was to assess the impact of a well-characterized extract from Citrus bergamia juice on adipogenesis and/or lipolysis using mesenchymal stem cells from human adipose tissue as a cell model. To evaluate the effects on adipogenesis, some cell cultures were treated with adipogenic medium plus 10 or 100 μg/mL of extract. To determine the properties on lipolysis, additional mesenchymal stem cells were cultured with adipogenic medium for 14 days and after this time added with Citrus bergamia for further 14 days. To verify adipogenic differentiation, oil red O staining at 7, 14, 21, and 28 days was performed. Moreover, the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ), adipocytes fatty acid-binding protein (A-FABP), adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL), hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), monoglyceride lipase (MGL), 5'-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK)α1/2, and pAMPKα1/2 was evaluated by Western blot analysis and the release of glycerol by colorimetric assay. Citrus bergamia extract suppressed the accumulation of intracellular lipids in mesenchymal stem cells during adipogenic differentiation and promoted lipolysis by repressing the expression of adipogenic genes and activating lipolytic genes. Citrus bergamia extract could be a useful natural product for improving adipose mobilization in obesity-related disorders.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

