Therapeutic Potential of Dental Pulp Stem Cell Secretome for Alzheimer's Disease Treatment: An In Vitro Study
- PMID: 27403169
- PMCID: PMC4923581
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/8102478
Therapeutic Potential of Dental Pulp Stem Cell Secretome for Alzheimer's Disease Treatment: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
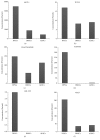
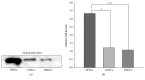
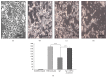
The secretome obtained from stem cell cultures contains an array of neurotrophic factors and cytokines that might have the potential to treat neurodegenerative conditions. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the most common human late onset and sporadic neurodegenerative disorders. Here, we investigated the therapeutic potential of secretome derived from dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) to reduce cytotoxicity and apoptosis caused by amyloid beta (Aβ) peptide. We determined whether DPSCs can secrete the Aβ-degrading enzyme, neprilysin (NEP), and evaluated the effects of NEP expression in vitro by quantitating Aβ-degrading activity. The results showed that DPSC secretome contains higher concentrations of VEGF, Fractalkine, RANTES, MCP-1, and GM-CSF compared to those of bone marrow and adipose stem cells. Moreover, treatment with DPSC secretome significantly decreased the cytotoxicity of Aβ peptide by increasing cell viability compared to nontreated cells. In addition, DPSC secretome stimulated the endogenous survival factor Bcl-2 and decreased the apoptotic regulator Bax. Furthermore, neprilysin enzyme was detected in DPSC secretome and succeeded in degrading Aβ 1-42 in vitro in 12 hours. In conclusion, our study demonstrates that DPSCs may serve as a promising source for secretome-based treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Figures




References
-
- Piermartiri T. C. B., Figueiredo C. P., Rial D., et al. Atorvastatin prevents hippocampal cell death, neuroinflammation and oxidative stress following amyloid-β 1 − 40 administration in mice: evidence for dissociation between cognitive deficits and neuronal damage. Experimental Neurology. 2010;226(2):274–284. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.08.030. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

