Segmentation of MRI Brain Images with an Improved Harmony Searching Algorithm
- PMID: 27403428
- PMCID: PMC4926041
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/4516376
Segmentation of MRI Brain Images with an Improved Harmony Searching Algorithm
Abstract
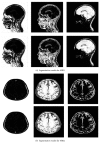
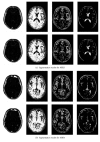
The harmony searching (HS) algorithm is a kind of optimization search algorithm currently applied in many practical problems. The HS algorithm constantly revises variables in the harmony database and the probability of different values that can be used to complete iteration convergence to achieve the optimal effect. Accordingly, this study proposed a modified algorithm to improve the efficiency of the algorithm. First, a rough set algorithm was employed to improve the convergence and accuracy of the HS algorithm. Then, the optimal value was obtained using the improved HS algorithm. The optimal value of convergence was employed as the initial value of the fuzzy clustering algorithm for segmenting magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain images. Experimental results showed that the improved HS algorithm attained better convergence and more accurate results than those of the original HS algorithm. In our study, the MRI image segmentation effect of the improved algorithm was superior to that of the original fuzzy clustering method.
Figures
References
-
- Liang Z. Tissue classification and segmentation of MR images. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine. 1993;12(1):81–85. doi: 10.1109/51.195944. - DOI
-
- Falcao A. X., Udupa J. K., Samarasekera S., Sharma S., Hirsch B. E., Lotufo R. D. A. User-steered image segmentation paradigms: live wire and live lane. Graphical Models and Image Processing. 1998;60(4):233–260. doi: 10.1006/gmip.1998.0475. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical