Knowledge and Attitude of Obstetric Care Providers on Partograph and Its Associated Factors in East Gojjam Zone, Northwest Ethiopia
- PMID: 27403453
- PMCID: PMC4923564
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/6913165
Knowledge and Attitude of Obstetric Care Providers on Partograph and Its Associated Factors in East Gojjam Zone, Northwest Ethiopia
Abstract
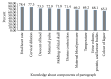
Introduction. Universal use of partograph is recommended during labor, to improve maternal and fetal outcome. The aim was to assess knowledge and attitude of obstetric caregivers about partograph and associated factors. Methods. Facility based cross-sectional study was conducted on 273 study participants. Study facilities and study units were selected using simple random sampling technique. Midwives, Nurses, Public Health Officers, Medical Doctors, and masters in Emergency Surgery and Obstetric were included in the study. Epi-data and SPSS statistical software were used. Results. About 153 (56.04%) and 150 (54.95%) of the obstetric caregivers had good knowledge and favorable attitude about partograph, respectively. Knowledge of partograph was significantly higher among obstetric caregivers that learnt about partograph during their College and who had received partograph on job training (AOR: 2.14, 95% C.I (1.17-3.93)) and (AOR: 2.25, 95% C.I (1.21-4.19)), respectively. Favorable attitude towards partograph was significantly higher among obstetrical caregivers who had training and learnt about partograph during their college (AOR: 3.37, 95% C.I (1.49-5.65)) and (AOR: 2.134, 95% C.I (1.175-3.877)), correspondingly. Conclusion. Above half of obstetric caregivers had good knowledge and a favorable attitude on partograph. The provision of on preservice and job training is necessary to improve caregivers' knowledge and attitude.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Trends in Maternal Mortality: 1990 to 2013, “Estimates by WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, The World Bank and the United Nations Population Division”. World Health Organization; 2014.
-
- Maternal Mortality Rates. A Tabulation of Available Information. 2nd. 1996. (WHO document FHE/86-3).
-
- USAID. Prevention of Prolonged and Obstructed Labor. 2004.
-
- World Health Organization. Trends in Maternal Mortality: 1990–2008. Estimates Developed by WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA and The World Bank. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2010.
-
- WHO/UNICEF/UNFPA. Maternal Mortality in 2000: Estimates Developed by the WHO, UNICEF and UNFPA. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2004.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources