Murine matrix metalloproteinase-20 overexpression stimulates cell invasion into the enamel layer via enhanced Wnt signaling
- PMID: 27403713
- PMCID: PMC4941722
- DOI: 10.1038/srep29492
Murine matrix metalloproteinase-20 overexpression stimulates cell invasion into the enamel layer via enhanced Wnt signaling
Abstract
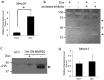
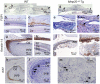
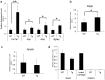
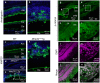
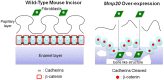
Matrix metalloproteinase-20 (MMP20) is expressed by ameloblasts in developing teeth and MMP20 mutations cause enamel malformation. We established a stably transfected Tet-Off Mmp20-inducible ameloblast-lineage cell line and found that MMP20 expression promoted cell invasion. Previously, we engineered transgenic mice (Tg) that drive Mmp20 expression and showed that Mmp20(+/+)Tg mice had soft enamel. Here we asked if Mmp20 overexpression disrupts ameloblast function. Incisors from Mmp20(+/+) mice expressing the Mmp20 Tg had a striking cell infiltrate which nearly replaced the entire enamel layer. A thin layer of enamel-like material remained over the dentin and at the outer tooth surface, but between these regions were invading fibroblasts and epithelial cells that surrounded ectopic bone-like calcifications. Mmp20(+/+)Tg mice had decreased enamel organ cadherin levels compared to the Mmp20 ablated and WT mice and, instead of predominantly locating adjacent to the ameloblast cell membrane, β-catenin was predominantly present within the nuclei of invading cells. Our data suggest that increased cadherin cleavage by transgenic MMP20 in the WT background releases excess β-catenin, which translocates to ameloblast nuclei to promote cell migration/invasion. Therefore, we conclude that MMP20 plays a role in normal ameloblast migration through tightly controlled Wnt signaling and that MMP20 overexpression disrupts this process.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MMP20 Overexpression Disrupts Molar Ameloblast Polarity and Migration.J Dent Res. 2018 Jul;97(7):820-827. doi: 10.1177/0022034518758657. Epub 2018 Feb 26. J Dent Res. 2018. PMID: 29481294 Free PMC article.
-
MMP20 modulates cadherin expression in ameloblasts as enamel develops.J Dent Res. 2013 Dec;92(12):1123-8. doi: 10.1177/0022034513506581. Epub 2013 Sep 25. J Dent Res. 2013. PMID: 24067343 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive activation of β-catenin in ameloblasts leads to incisor enamel hypomineralization.J Mol Histol. 2018 Oct;49(5):499-507. doi: 10.1007/s10735-018-9788-x. Epub 2018 Jul 31. J Mol Histol. 2018. PMID: 30066216
-
Modulation of cell-cell junctional complexes by matrix metalloproteinases.J Dent Res. 2013 Jan;92(1):10-7. doi: 10.1177/0022034512463397. Epub 2012 Oct 9. J Dent Res. 2013. PMID: 23053846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of KLK4 and MMP-20 in dental enamel formation.Biol Chem. 2008 Jun;389(6):695-700. doi: 10.1515/BC.2008.080. Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18627287 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MAST4 regulates stem cell maintenance with DLX3 for epithelial development and amelogenesis.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Jul;56(7):1606-1619. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01264-5. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38945953 Free PMC article.
-
MMP20 Overexpression Disrupts Molar Ameloblast Polarity and Migration.J Dent Res. 2018 Jul;97(7):820-827. doi: 10.1177/0022034518758657. Epub 2018 Feb 26. J Dent Res. 2018. PMID: 29481294 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-Induced Fam83h Knock-out Leads to Impaired Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway and Altered Expression of Tooth Mineralization Genes in Mice.Iran J Biotechnol. 2023 Oct 1;21(4):e3673. doi: 10.30498/ijb.2023.391902.3673. eCollection 2023 Oct. Iran J Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38269199 Free PMC article.
-
Intertwined Signaling Pathways Governing Tooth Development: A Give-and-Take Between Canonical Wnt and Shh.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 29;9:758203. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.758203. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34778267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ADAM10 is Expressed by Ameloblasts, Cleaves the RELT TNF Receptor Extracellular Domain and Facilitates Enamel Development.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 1;9(1):14086. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50277-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31575895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roycik M. D., Fang X. & Sang Q. X. A fresh prospect of extracellular matrix hydrolytic enzymes and their substrates. Curr Pharm Des 15, 1295–1308 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Bartlett J. D., Ryu O. H., Xue J., Simmer J. P. & Margolis H. C. Enamelysin mRNA displays a developmentally defined pattern of expression and encodes a protein which degrades amelogenin. Connect Tissue Res 39, 101–109, discussion 141-109 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Bartlett J. D. & Simmer J. P. Proteinases in developing dental enamel. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 10, 425–441 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Fukae M. et al.. Enamelysin (matrix metalloproteinase-20): localization in the developing tooth and effects of pH and calcium on amelogenin hydrolysis. J Dent Res 77, 1580–1588 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Begue-Kirn C., Krebsbach P. H., Bartlett J. D. & Butler W. T. Dentin sialoprotein, dentin phosphoprotein, enamelysin and ameloblastin: tooth-specific molecules that are distinctively expressed during murine dental differentiation. Eur J Oral Sci 106, 963–970 (1998). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

