Evaluation of short synthetic antimicrobial peptides for treatment of drug-resistant and intracellular Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 27405275
- PMCID: PMC4942614
- DOI: 10.1038/srep29707
Evaluation of short synthetic antimicrobial peptides for treatment of drug-resistant and intracellular Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
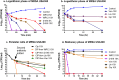
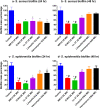
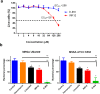
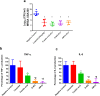
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections present a serious challenge because of the emergence of resistance to numerous conventional antibiotics. Due to their unique mode of action, antimicrobial peptides are novel alternatives to traditional antibiotics for tackling the issue of bacterial multidrug resistance. Herein, we investigated the antibacterial activity of two short novel peptides (WR12, a 12 residue peptide composed exclusively of arginine and tryptophan, and D-IK8, an eight residue β-sheet peptide) against multidrug resistant staphylococci. In vitro, both peptides exhibited good antibacterial activity against MRSA, vancomycin-resistant S. aureus, linezolid-resistant S. aureus, and methicillin-resistant S. epidermidis. WR12 and D-IK8 were able to eradicate persisters, MRSA in stationary growth phase, and showed significant clearance of intracellular MRSA in comparison to both vancomycin and linezolid. In vivo, topical WR12 and D-IK8 significantly reduced both the bacterial load and the levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in MRSA-infected skin lesions. Moreover, both peptides disrupted established in vitro biofilms of S. aureus and S. epidermidis significantly more so than traditional antimicrobials tested. Taken together, these results support the potential of WR12 and D-IK8 to be used as a topical antimicrobial agent for the treatment of staphylococcal skin infections.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibacterial activity and therapeutic efficacy of Fl-P(R)P(R)P(L)-5, a cationic amphiphilic polyproline helix, in a mouse model of staphylococcal skin infection.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Oct 22;9:5749-54. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S94505. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26543355 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing auranofin for the treatment of cutaneous staphylococcal infections.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016 Mar;47(3):195-201. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2015.12.016. Epub 2016 Jan 23. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016. PMID: 26895605 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial activity of novel cationic peptides against clinical isolates of multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius from infected dogs.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 31;9(12):e116259. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116259. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25551573 Free PMC article.
-
European perspective and update on the management of complicated skin and soft tissue infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus after more than 10 years of experience with linezolid.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014 Apr;20 Suppl 4:3-18. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12463. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014. PMID: 24580738 Review.
-
Beyond conventional antibiotics for the future treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: two novel alternatives.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012 Aug;65(3):399-412. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2012.00954.x. Epub 2012 Apr 4. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22409572 Review.
Cited by
-
The Bactericidal Activity of Temporin Analogues Against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 25;20(19):4761. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194761. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31557917 Free PMC article.
-
Photolysis of Staphyloxanthin in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Potentiates Killing by Reactive Oxygen Species.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019 Mar 30;6(11):1900030. doi: 10.1002/advs.201900030. eCollection 2019 Jun 5. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019. PMID: 31179216 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides and Cell-Penetrating Peptides for Treating Intracellular Bacterial Infections.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Feb 5;10:612931. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.612931. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33614528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delivered baicalein immunomodulatory hydrogel with dual properties of pH-responsive and anti-infection orchestrates pro-regenerative response of macrophages for enhanced hypertrophic scars therapy.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jul 31;34:102160. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102160. eCollection 2025 Oct. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40822925 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophage-encoded lethal membrane disruptors: Advances in understanding and potential applications.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 26;13:1044143. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1044143. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36345304 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wolcott R. D. et al.. Chronic wounds and the medical biofilm paradigm. Journal of wound care 19, 45–46, 48–50, 52–43 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Kresken M., Hafner D., Schmitz F. J., Wichelhaus T. A. & Paul-Ehrlich-Society for, C. Prevalence of mupirocin resistance in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis: results of the Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Study of the Paul-Ehrlich-Society for Chemotherapy, 2001. International journal of antimicrobial agents 23, 577–581, 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2003.11.007 (2004). - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schauber J. & Gallo R. L. Antimicrobial peptides and the skin immune defense system. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 122, 261–266, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2008.03.027 (2008). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

