Molecular diagnosis of pediatric patients with citrin deficiency in China: SLC25A13 mutation spectrum and the geographic distribution
- PMID: 27405544
- PMCID: PMC4942605
- DOI: 10.1038/srep29732
Molecular diagnosis of pediatric patients with citrin deficiency in China: SLC25A13 mutation spectrum and the geographic distribution
Abstract
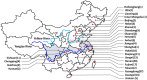
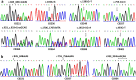
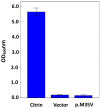
Citrin deficiency (CD) is a Mendelian disease due to biallelic mutations of SLC25A13 gene. Neonatal intrahepatic cholestasis caused by citrin deficiency (NICCD) is the major pediatric CD phenotype, and its definite diagnosis relies on SLC25A13 genetic analysis. China is a vast country with a huge population, but the SLC25A13 genotypic features of CD patients in our country remains far from being well clarified. Via sophisticated molecular analysis, this study diagnosed 154 new CD patients in mainland China and identified 9 novel deleterious SLC25A13 mutations, i.e. c.103A > G, [c.329 - 154_c.468 + 2352del2646; c.468 + 2392_c.468 + 2393ins23], c.493C > T, c.755 - 1G > C, c.845_c.848 + 1delG, c.933_c.933 + 1insGCAG, c.1381G > T, c.1452 + 1G > A and c.1706_1707delTA. Among the 274 CD patients diagnosed by our group thus far, 41 SLC25A13 mutations/variations were detected. The 7 mutations c.775C > T, c.851_854del4, c.1078C > T, IVS11 + 1G > A, c.1364G > T, c.1399C > T and IVS16ins3kb demonstrated significantly different geographic distribution. Among the total 53 identified genotypes, only c.851_854del4/c.851_854del4 and c.851_854del4/c.1399C > T presented different geographic distribution. The northern population had a higher level of SLC25A13 allelic heterogeneity than those in the south. These findings enriched the SLC25A13 mutation spectrum and brought new insights into the geographic distribution of the variations and genotypes, providing reliable evidences for NICCD definite diagnosis and for the determination of relevant molecular targets in different Chinese areas.
Figures

References
-
- Kobayashi K. et al.. The gene mutated in adult-onset type II citrullinaemia encodes a putative mitochondrial carrier protein. Nat Genet. 22, 159–163 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Palmieri F. Mitochondrial transporters of the SLC25 family and associated diseases: a review. J Inherit Metab Dis. 37, 565–575 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Palmieri F. & Monné M. Discoveries, metabolic roles and diseases of mitochondrial carriers: A review. Biochim Biophys Acta. pii: S0167-4889(16)30060-X (2016). - PubMed
-
- Tomomasa T. et al.. Possible clinical and histologic manifestations of adult-onset type II citrullinemia in early infancy. J Pediatr. 138, 741–743 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

