A whole-genome sequence and transcriptome perspective on HER2-positive breast cancers
- PMID: 27406316
- PMCID: PMC4947184
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12222
A whole-genome sequence and transcriptome perspective on HER2-positive breast cancers
Abstract
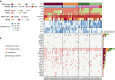
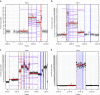
HER2-positive breast cancer has long proven to be a clinically distinct class of breast cancers for which several targeted therapies are now available. However, resistance to the treatment associated with specific gene expressions or mutations has been observed, revealing the underlying diversity of these cancers. Therefore, understanding the full extent of the HER2-positive disease heterogeneity still remains challenging. Here we carry out an in-depth genomic characterization of 64 HER2-positive breast tumour genomes that exhibit four subgroups, based on the expression data, with distinctive genomic features in terms of somatic mutations, copy-number changes or structural variations. The results suggest that, despite being clinically defined by a specific gene amplification, HER2-positive tumours melt into the whole luminal-basal breast cancer spectrum rather than standing apart. The results also lead to a refined ERBB2 amplicon of 106 kb and show that several cases of amplifications are compatible with a breakage-fusion-bridge mechanism.
Figures

References
-
- Slamon D. J. et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N. Engl. J. Med. 344, 783–792 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Marty M. et al. Randomized phase II trial of the efficacy and safety of trastuzumab combined with docetaxel in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer administered as first-line treatment: the M77001 study group. J. Clin. Oncol. 23, 4265–4274 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Romond E. H. et al. Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 353, 1673–1684 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

