Adaptive Randomization of Neratinib in Early Breast Cancer
- PMID: 27406346
- PMCID: PMC5259558
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1513750
Adaptive Randomization of Neratinib in Early Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: The heterogeneity of breast cancer makes identifying effective therapies challenging. The I-SPY 2 trial, a multicenter, adaptive phase 2 trial of neoadjuvant therapy for high-risk clinical stage II or III breast cancer, evaluated multiple new agents added to standard chemotherapy to assess the effects on rates of pathological complete response (i.e., absence of residual cancer in the breast or lymph nodes at the time of surgery).
Methods: We used adaptive randomization to compare standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus the tyrosine kinase inhibitor neratinib with control. Eligible women were categorized according to eight biomarker subtypes on the basis of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status, hormone-receptor status, and risk according to a 70-gene profile. Neratinib was evaluated against control with regard to 10 biomarker signatures (prospectively defined combinations of subtypes). The primary end point was pathological complete response. Volume changes on serial magnetic resonance imaging were used to assess the likelihood of such a response in each patient. Adaptive assignment to experimental groups within each disease subtype was based on Bayesian probabilities of the superiority of the treatment over control. Enrollment in the experimental group was stopped when the 85% Bayesian predictive probability of success in a confirmatory phase 3 trial of neoadjuvant therapy reached a prespecified threshold for any biomarker signature ("graduation"). Enrollment was stopped for futility if the probability fell to below 10% for every biomarker signature.
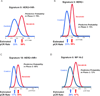
Results: Neratinib reached the prespecified efficacy threshold with regard to the HER2-positive, hormone-receptor-negative signature. Among patients with HER2-positive, hormone-receptor-negative cancer, the mean estimated rate of pathological complete response was 56% (95% Bayesian probability interval [PI], 37 to 73%) among 115 patients in the neratinib group, as compared with 33% among 78 controls (95% PI, 11 to 54%). The final predictive probability of success in phase 3 testing was 79%.
Conclusions: Neratinib added to standard therapy was highly likely to result in higher rates of pathological complete response than standard chemotherapy with trastuzumab among patients with HER2-positive, hormone-receptor-negative breast cancer. (Funded by QuantumLeap Healthcare Collaborative and others; I-SPY 2 TRIAL ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01042379.).
Figures


Comment in
-
I-SPY 2--A Glimpse of the Future of Phase 2 Drug Development?N Engl J Med. 2016 Jul 7;375(1):7-9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1602256. N Engl J Med. 2016. PMID: 27406345 No abstract available.
-
I-SPY 2--Toward More Rapid Progress in Breast Cancer Treatment.N Engl J Med. 2016 Jul 7;375(1):83-4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1603691. N Engl J Med. 2016. PMID: 27406352 No abstract available.
-
Adaptive Randomization of Neratinib in Early Breast Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2016 Oct 20;375(16):1592-3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1609993. N Engl J Med. 2016. PMID: 27797314 No abstract available.
-
Adaptive Randomization of Neratinib in Early Breast Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2016 Oct 20;375(16):1592. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1609993. N Engl J Med. 2016. PMID: 28103001 No abstract available.
-
Adaptive Randomization of Neratinib in Early Breast Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2016 Oct 20;375(16):1593-4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1609993. N Engl J Med. 2016. PMID: 28103002 No abstract available.
References
-
- Berry DA. Adaptive clinical trials in oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;9(4):199–207. - PubMed
-
- Rugo H, Olopade O, DeMichele A, et al. Abstract S5-02: Veliparib/carboplatin plus standard neoadjuvant therapy for high-risk breast cancer: First efficacy results from the I-SPY 2 TRIAL. Cancer Res. 2014;73(24 Supplement) S5–02 – S5–02.
-
- Tripathy D, Chien AJ, Hylton NM, Buxton MB, Ewing CA, Wallace AM, Forero A, Kaplan HG, Nanda R, Albain KS, Moulder SL, Haley BB, DeMichele A, Symmans WF, van ’t Veer L Paoloni MDMI-S 2 TC. Adaptively randomized trial of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without the Akt inhibitor MK-2206: Graduation results from the I-SPY 2 Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(suppl) abstr 524.
-
- Kümler I, Tuxen MK, Nielsen DL. A systematic review of dual targeting in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014;40(2):259–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
