An investigation of BMP-7 mediated alterations to BMP signalling components in human tenocyte-like cells
- PMID: 27406972
- PMCID: PMC4942578
- DOI: 10.1038/srep29703
An investigation of BMP-7 mediated alterations to BMP signalling components in human tenocyte-like cells
Abstract
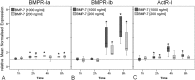
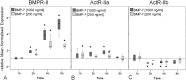
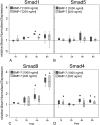
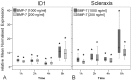
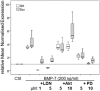
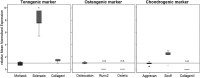
The incidence of tendon re-tears post-surgery is an ever present complication. It is suggested that the application of biological factors, such as bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP-7), can reduce complication rates by promoting tenogenic characteristics in in vitro studies. However, there remains a dearth of information in regards to the mechanisms of BMP-7 signalling in tenocytes. Using primary human tenocyte-like cells (hTLCs) from the supraspinatus tendon the BMP-7 signalling pathway was investigated: induction of the BMP associated Smad pathway and non-Smad pathways (AKT, p38, ERK1/2 and JNK); alterations in gene expression of BMP-7 associated receptors, Smad pathway components, Smad target gene (ID1) and tenogenic marker scleraxis. BMP-7 increases the expression of specific BMP associated receptors, BMPR-Ib and BMPR-II, and Smad8. Additionally, BMP-7 activates significantly Smad1/5/8 and slightly p38 pathways as indicated by an increase in phosphorylation and proven by inhibition experiments, where p-ERK1/2 and p-JNK pathways remain mainly unresponsive. Furthermore, BMP-7 increases the expression of the Smad target gene ID1, and the tendon specific transcription factor scleraxis. The study shows that tenocyte-like cells undergo primarily Smad8 and p38 signalling after BMP-7 stimulation. The up-regulation of tendon related marker genes and matrix proteins such as Smad8/9, scleraxis and collagen I might lead to positive effects of BMP-7 treatment for rotator cuff repair, without significant induction of osteogenic and chondrogenic markers.
Figures


References
-
- Aydin N., Kocaoglu B. & Guven O. “Single-row versus double-row arthroscopic rotator cuff repair in small- to medium-sized tears”, J. Shoulder. Elbow. Surg. 19(5), 722–725 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Gerhardt C. et al. “Arthroscopic single-row modified mason-allen repair versus double-row suture bridge reconstruction for supraspinatus tendon tears: a matched-pair analysis”, Am. J. Sports Med. 40(12), 2777–2785 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Klatte-Schulz F. et al. “Relationship between muscle fatty infiltration and the biological characteristics and stimulation potential of tenocytes from rotator cuff tears”, J. Orthop. Res. 32(1), 129–137 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Klatte-Schulz F. et al. “Influence of age on the cell biological characteristics and the stimulation potential of male human tenocyte-like cells”, Eur. Cell Mater. 24, 74–89 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

