Culture media optimization of Porphyridium purpureum: production potential of biomass, total lipids, arachidonic and eicosapentaenoic acid
- PMID: 27407193
- PMCID: PMC4921077
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-016-2185-0
Culture media optimization of Porphyridium purpureum: production potential of biomass, total lipids, arachidonic and eicosapentaenoic acid
Abstract
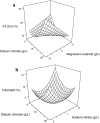
Porphyridium purpureum a red marine microalga is known for phycobiliproteins (PB), polyunsaturated fatty acids and sulphated exopolysaccharides. In the present study, effects of media constituents for the production of different polyunsaturated fatty acids from P. purpureum were considered using a response surface methodology (RSM). A second order polynomial was used to predict the response functions in terms of the independent variables such as the concentrations of sodium chloride, magnesium sulphate, sodium nitrate and potassium dihydrogen phosphate. The response functions were production of biomass yield, total lipid and polyunsaturated fatty acids like arachidonic acid (AA 20:4) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA 20:5). Results corroborated that maximum Biomass (0.95 gL(-1)) yield was at the concentrations of sodium chloride (14.89 gL(-1)), magnesium sulfate (3.93 gL(-1)) and sodium nitrate (0.96 gL(-1)) and potassium dihydrogen phosphate (0.09 gL(-1)). Optimum total lipid (17.9 % w/w) and EPA (34.6 % w/w) content was at the concentrations of sodium chloride (29.98 gL(-1)), magnesium sulfate (9.34 gL(-1)) and sodium nitrate (1.86 gL(-1)). Variation in concentration of potassium dihydrogen phosphate for both lipid (0.01gL(-1)) and EPA content (0.20 gL(-1)) was observed. The optimum conditions for biomass, total lipid, AA and EPA varied indicating their batch mode of growth and interaction effect of the salt.
Keywords: Eicosapentaenoic acid; Fatty acids; Optimization; Porphyridium; Response surface methodology (RSM).
Figures


References
-
- Adda M, Merchuk JC, Arad S. Effect of nitrate on growth and production of cell wall polysaccharide by the unicellular red alga Porphyridium. Biomass. 1986;10:131–140. doi: 10.1016/0144-4565(86)90061-2. - DOI
-
- Apt KE, Behrens PW. Commercial developments in microalgal biotechnology. J Phycol. 1996;35:215–226. doi: 10.1046/j.1529-8817.1999.3520215.x. - DOI
-
- Bhattacharya S, Prakash M. Extrusion cooking of blends of rice and chickpea flour: a response surface analysis. J. Food Eng. 1994;21:315–330. doi: 10.1016/0260-8774(94)90076-0. - DOI
-
- Borowitzka MA. Commercial production of microalgae: ponds, tanks, tubes and fermenters. J Biotechnol. 1999;70:313–321. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1656(99)00083-8. - DOI
-
- Carvalho AP, Malcata FX (2000) Effect of culture media on production of polyunsaturated fatty acids by Pavlova lutheri. Cryptogam Algol 21:59–71
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
