Ultrasonography in Patients with Suspected Acute Appendicitis
- PMID: 27407771
- PMCID: PMC4925633
- DOI: 10.1016/S0377-1237(05)80166-2
Ultrasonography in Patients with Suspected Acute Appendicitis
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the usefulness and limitations of graded compression ultrasonography in the diagnosis of clinically equivocal cases of suspected acute appendicitis at the setting of mid zonal military hospital of India.
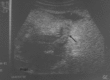
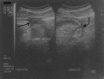
Methods: A prospective study, graded compression ultrasonography with self localization was carried out with 3.5 MHz convex, 5 MHz convex and 7.5 MHz linear transducers (Wipro GE) in 69 clinically equivocal suspected cases of acute appendicitis. With maximal compression the anteroposterior diameter of appendix was measured from outer to outer wall. The main criterion for diagnosing appendicitis was demonstration of a non compressible appendix with anteroposterior dimension of 7mm or more.
Result: Sonologically 36 (52%) cases were diagnosed as appendicitis. Anteroposterior outer diameter of inflamed appendices ranged from 7mm to 21mm (mean 10.5mm). 30 (83%) of 36 patients could accurately self localize the point of maximum tenderness. There were 01 false positive and 04 false negative cases. Sensitivity and specificity were 89.7% and 96.6% respectively. Positive and negative predictive values were 97.2% and 87.8% respectively. Alternative diagnoses were offered in 33 (47.8%) cases. Amongst these 33 cases, 14(42.4%) had abdominal pain of unknown origin. Gynaecologic, urologic and gastrointestinal aetiologies were established in 10(30.3%), 07(21.2%) and 02(6%) cases respectively.
Conclusion: Graded compression ultrasonography superadded with self localization is an accurate means of diagnosing/excluding appendicitis in clinically equivocal cases of acute appendicitis and it is of great value in establishing alternative diagnoses.
Keywords: Acute appendicitis; Ultrasonography.
Figures

References
-
- Puylaert JB. Acute appendicitis. US evaluation using graded compression. Radiology. 1986;158:355–360. - PubMed
-
- Chesbrough RM, Burkhard TK, Balsara ZN, Goff WB, Davis DJ. Self-localisation in US of appendicitis an addition to graded compression. Radiology. 1993;187:349–351. - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum BA, Wilson SR. Appendicitis at the millennium. Radiology. 2000;215(2):337–348. - PubMed
-
- Paulson EK, Kalady MF, Pappas TN. Suspected appendicitis. New Engl J of Med. 2003;348(3):236–242. - PubMed
-
- Yacoe ME, Jeffrey RB., Jr Sonography of appendicitis and diverticulitis. Radiologic Clinics of North America. 1994;32(5):899–912. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

