Serum Serotonin Abnormality in Depression
- PMID: 27408213
- PMCID: PMC4921409
- DOI: 10.1016/S0377-1237(09)80120-2
Serum Serotonin Abnormality in Depression
Abstract
Background: Serotonin plays an important role in treatment of depression. We evaluated the clinical correlates of plasma serotonin levels in depressed patients before and after treatment.
Methods: Study sample comprised of 40 patients diagnosed on ICD-10 diagnostic criteria, and an equal number of healthy matched controls. Subjects were evaluated on Beck's Depression Inventory (BDI) and Suicide Ideation Scale (SIS), before and after the treatment. Blood samples were collected from all the cases and controls before starting the antidepressant medication with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI's). Serum serotonin levels were measured before and after treatment.
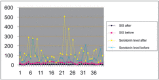
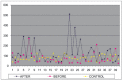
Result: Significant differences in scores before and after the intervention on BDI, SIS and serotonin levels of cases and controls (p<.000) were noted. Correlation between the serum serotonin levels before and after the treatment, and between the rating scales did not reveal significant association (p > 0.05). Patients with suicidal intentions had lower levels of serotonin. The scores changed after intervention.
Conclusion: Treatment with SSRI's had shown significant changes in clinical conditions. However these changes did not relate significantly with serum serotonin levels.
Keywords: Depression; Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; Serotonin.
Figures

References
-
- Schildkraut JJ. The catecholamine hypothesis of affective disorders: A review of supporting evidence. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1965;7:524–533. - PubMed
-
- Schloss P, Williams DC. The serotonin transporter: a primary target for antidepressant drugs Biochemistry Department University of Dublin, Trinity College Ireland. J Psychopharmacol. 1998;12(2):115–1521. - PubMed
-
- Jaffe R. Tryptophan Update: Helpful Adjunct and Innocent Bystander. J of Nutrition Medicine. 1994;4:133–139.
-
- Skop B, Finkelstein J, Mareth T, Magoon M, Brown T. An over the counter cold remedy & vascular disease. Am J Emerg Med. 1994;12:646–648. - PubMed
-
- Mills KC. Serotonin syndrome. Am Fam Physician. 1995;52:1475–1482. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

