Infective endocarditis caused by Streptococcus tigurinus-like organisms
- PMID: 27408744
- PMCID: PMC4932624
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nmni.2016.05.012
Infective endocarditis caused by Streptococcus tigurinus-like organisms
Abstract
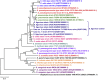
Streptococcus species are important causes of infective endocarditis but species identification remains challenging. We report two cases of infective endocarditis due to Streptococcus tigurinus-like organisms, which were first identified by 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequence analysis and subsequently confirmed using phylogeny based on the analysis of the shetA gene encoding exfoliative toxin.
Keywords: 16S rRNA; PCR; Streptococcus tigurinus; endocarditis; shet A gene.
Figures
References
-
- Zbinden A., Mueller N.J., Tarr P.E., Sproer C., Keller P.M., Bloemberg G.V. Streptococcus tigurinus sp. nov., isolated from blood of patients with endocarditis, meningitis and spondylodiscitis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2012;62:2941–2945. - PubMed
-
- Bessède E., Angla-Gre M., Delagarde Y., Sep Hieng S., Ménard A., Mégraud F. Matrix-assisted laser-desorption/ionization biotyper: experience in the routine of a University hospital. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17:533–538. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
