Evaluation of Simultaneous Dual-radioisotope SPECT Imaging Using (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose and (99m)Tc-tetrofosmin
- PMID: 27408894
- PMCID: PMC4938876
- DOI: 10.7508/aojnmb.2016.02.002
Evaluation of Simultaneous Dual-radioisotope SPECT Imaging Using (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose and (99m)Tc-tetrofosmin
Abstract
Objectives: Use of a positron emission tomography (PET)/single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) system facilitates the simultaneous acquisition of images with fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose ((18)F-FDG) and technetium ((99m)Tc)-tetrofosmin. However, (18)F has a short half-life, and 511 keV Compton-scattered photons are detected in the (99m)Tc energy window. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to investigate the consequences of these facts.
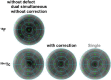
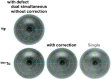
Methods: The crosstalk correction for images in the (99m)Tc energy window involved the dual energy window (DEW) subtraction method. In phantom studies, changes in the count of uniform parts in a phantom (due to attenuation from decay), signal detectability in the hot-rod part of the phantom, and the defect contrast ratio in a cardiac phantom were examined.
Results: For (18)F-FDG in the step-and-shoot mode, nearly a 9% difference was observed in the count of projection data between the start and end positions of acquisition in the uniform part of the phantom. Based on the findings, the detectability of 12 mm hot rods was relatively poor. In the continuous acquisition mode, the count difference was corrected, and detectability of the hot rods was improved. The crosstalk from (18)F to the (99m)Tc energy window was approximately 13%. In the cardiac phantom, the defect contrast in (99m)Tc images from simultaneous dual-radionuclide acquisition was improved by approximately 9% after DEW correction; the contrast after correction was similar to acquisition with (99m)Tc alone.
Conclusion: Based on the findings, the continuous mode is useful for (18)F-FDG acquisition, and DEW crosstalk correction is necessary for (99m)Tc-tetrofosmin imaging.
Keywords: 18F-FDG; 99mTc-tetrofosmin; DEW method; PET/SPECT system.
Figures





References
-
- Japan Radioisotope Association. The Present State of Nuclear Medicine Practice in Japan—A Report of the 7th Nationwide Survey in 2012. Radioisotopes. 2013;62(8):545–608.
-
- Coleman RE, Laymon CM, Turkington TG. FDG imaging of lung nodules:a phantom study comparing SPECT, camera-based PET, and delicated PET. Radiology. 1999;210(3):823–8. - PubMed
-
- van Lingen A, Huijgens PC, Visser FC, Ossenkoppele GJ, Hoekstra OS, Martens HJ, et al. Performance characteristics of a 511-keV collimator for imaging positron emitters with a standard gamma-camera. Eur J Nucl Med. 1992;19(5):315–21. - PubMed
-
- Fukuchi K, Katafuchi T, Fukushima K, Shimotsu Y, Toba M, Hayashida K, et al. Estimation of myocardial perfusion and viability using simultaneous 99mTc-Tetrofosmin--FDG collimated SPECT. J Nucl Med. 2000;41(8):1318–23. - PubMed
-
- Pagnanelli RA, Hanson MW, Turkington T, Coleman RE, Borges-Neto S. Gated 99mTc-Tetrofosmin and 18F-FDG studies:a comparison of single-acquisition and separate-acquisition protocols. J Nucl Med Technol. 2002;30(4):175–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
