YAP promotes erlotinib resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer cells
- PMID: 27409162
- PMCID: PMC5239524
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10458
YAP promotes erlotinib resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer cells
Abstract
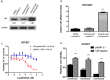
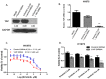
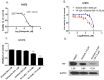
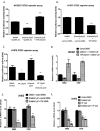
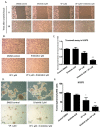
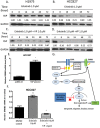
Yes-associated protein (YAP) is a main mediator of the Hippo pathway, which promotes cancer development. Here we show that YAP promotes resistance to erlotinib in human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. We found that forced YAP overexpression through YAP plasmid transfection promotes erlotinib resistance in HCC827 (exon 19 deletion) cells. In YAP plasmid-transfected HCC827 cells, GTIIC reporter activity and Hippo downstream gene expression of AREG and CTGF increased significantly (P<0.05), as did ERBB3 mRNA expression (P<0.05). GTIIC reporter activity, ERBB3 protein and mRNA expression all increased in HCC827 erlotinib-resistance (ER) cells compared to parental HCC827 cells. Inhibition of YAP by small interfering RNA (siRNA) increased the cytotoxicity of erlotinib to H1975 (L858R+T790M) cells. In YAP siRNA-transfected H1975 cells, GTIIC reporter activity and downstream gene expression of AREG and CTGF decreased significantly (P<0.05). Verteporfin, YAP inhibitor had an effect similar to that of YAP siRNA; it increased sensitivity of H1975 cells to erlotinib and in combination with erlotinib, synergistically reduced migration, invasion and tumor sphere formation abilities in H1975 cells. Our results indicate that YAP promotes erlotinib resistance in the erlotinib-sensitive NSCLC cell line HCC827. Inhibition of YAP by siRNA increases sensitivity of erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cell line H1975 to erlotinib.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) resistance; erlotinib; non-small cell lung cancer; yes-associated protein.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of ERK1/2 down-regulates the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway in human NSCLC cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 28;6(6):4357-68. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2974. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25738359 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer to erlotinib is regulated by the Notch/miR-223/FBXW7 pathway.Biosci Rep. 2017 Jun 21;37(3):BSR20160478. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160478. Print 2017 Jun 30. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28507201 Free PMC article.
-
Erlotinib-induced autophagy in epidermal growth factor receptor mutated non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2013 Sep;81(3):354-361. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.05.012. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Lung Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23769318
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Pathway, Yes-Associated Protein (YAP) and the Regulation of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 5;20(15):3821. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153821. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31387256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YAP at the Crossroads of Biomechanics and Drug Resistance in Human Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 6;24(15):12491. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512491. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569866 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The YAP1-NMU Axis Is Associated with Pancreatic Cancer Progression and Poor Outcome: Identification of a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Sep 30;11(10):1477. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101477. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31575084 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of yes-associated protein down-regulates PD-L1 (CD274) expression in human malignant pleural mesothelioma.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Jun;22(6):3139-3148. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13593. Epub 2018 Mar 24. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29575535 Free PMC article.
-
A New Player in Neuroblastoma: YAP and Its Role in the Neuroblastoma Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Sep 16;13(18):4650. doi: 10.3390/cancers13184650. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34572875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Yes1 Associated Transcriptional Regulator Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Improves Sensitivity to Sorafenib: An in vitro and in vivo Study.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Oct 29;13:11071-11087. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S249412. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33149619 Free PMC article.
-
The novel BET degrader, QCA570, is highly active against the growth of human NSCLC cells and synergizes with osimertinib in suppressing osimertinib-resistant EGFR-mutant NSCLC cells.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Feb 15;12(2):779-792. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35261801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:169–81. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R, Pallares C, Sanchez JM, Porta R, Cobo M, Garrido P, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239–46. - PubMed
-
- Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, Feng J, Liu XQ, Wang C, Zhang S, Wang J, Zhou S, Ren S, Lu S, Zhang L, Hu C, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:735–42. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

