Comprehensive profiling and quantitation of oncogenic mutations in non small-cell lung carcinoma using single molecule amplification and re-sequencing technology
- PMID: 27409166
- PMCID: PMC5226597
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10464
Comprehensive profiling and quantitation of oncogenic mutations in non small-cell lung carcinoma using single molecule amplification and re-sequencing technology
Abstract
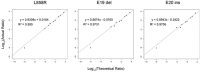
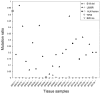
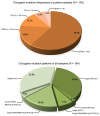
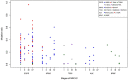
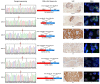
Activating and resistance mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of several oncogenes are frequently associated with non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). In this study we assessed the frequency, type and abundance of EGFR, KRAS, BRAF, TP53 and ALK mutations in tumour specimens from 184 patients with early and late stage disease using single molecule amplification and re-sequencing technology (SMART). Based on modelling of EGFR mutations, the detection sensitivity of the SMART assay was at least 0.1%. Benchmarking EGFR mutation detection against the gold standard ARMS-PCR assay, SMART assay had a sensitivity and specificity of 98.7% and 99.0%. Amongst the 184 samples, EGFR mutations were the most prevalent (59.9%), followed by KRAS (16.9%), TP53 (12.7%), EML4-ALK fusions (6.3%) and BRAF (4.2%) mutations. The abundance and types of mutations in tumour specimens were extremely heterogeneous, involving either monoclonal (51.6%) or polyclonal (12.6%) mutation events. At the clinical level, although the spectrum of tumour mutation(s) was unique to each patient, the overall patterns in early or advanced stage disease were relatively similar. Based on these findings, we propose that personalized profiling and quantitation of clinically significant oncogenic mutations will allow better classification of patients according to tumour characteristics and provide clinicians with important ancillary information for treatment decision-making.
Keywords: allele-specific amplification refractory mutation system; non small-cell lung carcinoma; oncogenic mutations; single molecule amplification and re-sequencing technology.
Conflict of interest statement
YS, JZ, MX and DSC are employees of Berry Genomic Corporation, Beijing
Figures
References
-
- Zhou JX, Yang H, Deng Q, Gu X, He P, Lin Y, Zhao M, Jiang J, Chen H, Lin Y, Yin W, Mo L, He J. Oncogenic driver mutations in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer at various clinical stages. Ann Oncol. 2013;24:1319–1325. - PubMed
-
- Black RC, Khurshid H. NSCLC: An Update of Driver Mutations, Their Role in Pathogenesis and Clinical Significance. R I Med J (2013) 2015;98:25–28. - PubMed
-
- Devarakonda S, Morgensztern D, Govindan R. Genomic alterations in lung adenocarcinoma. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:e342–e351. - PubMed
-
- Califano R, Abidin A, Tariq NU, Economopoulou P, Metro G, Mountzios G. Beyond EGFR and ALK inhibition: unravelling and exploiting novel genetic alterations in advanced non small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015;41:401–411. - PubMed
-
- Rikova K, Guo A, Zeng Q, Possemato A, Yu J, Haack H, Nardone J, Lee K, Reeves C, Li Y, Hu Y, Tan Z, Stokes M, et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell. 2007;131:1190–1203. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

