The miR-644a/CTBP1/p53 axis suppresses drug resistance by simultaneous inhibition of cell survival and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer
- PMID: 27409664
- PMCID: PMC5226553
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10489
The miR-644a/CTBP1/p53 axis suppresses drug resistance by simultaneous inhibition of cell survival and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer
Abstract
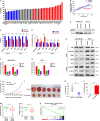
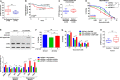
Tumor cells develop drug resistance which leads to recurrence and distant metastasis. MicroRNAs are key regulators of tumor pathogenesis; however, little is known whether they can sensitize cells and block metastasis simultaneously. Here, we report miR-644a as a novel inhibitor of both cell survival and EMT whereby acting as pleiotropic therapy-sensitizer in breast cancer. We showed that both miR-644a expression and its gene signature are associated with tumor progression and distant metastasis-free survival. Mechanistically, miR-644a directly targets the transcriptional co-repressor C-Terminal Binding Protein 1 (CTBP1) whose knock-outs by the CRISPR-Cas9 system inhibit tumor growth, metastasis, and drug resistance, mimicking the phenotypes induced by miR-644a. Furthermore, downregulation of CTBP1 by miR-644a upregulates wild type- or mutant-p53 which acts as a 'molecular switch' between G1-arrest and apoptosis by inducing cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 (p21, CDKN1A, CIP1) or pro-apoptotic phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1 (Noxa, PMAIP1), respectively. Interestingly, an increase in mutant-p53 by either overexpression of miR-644a or downregulation of CTBP1 was enough to shift this balance in favor of apoptosis through upregulation of Noxa. Notably, p53-mutant patients, but not p53-wild type ones, with high CTBP1 have a shorter survival suggesting that CTBP1 could be a potential prognostic factor for breast cancer patients with p53 mutations. Overall, re-activation of the miR-644a/CTBP1/p53 axis may represent a new strategy for overcoming both therapy resistance and metastasis.
Keywords: CTBP1; EMT; miRNAs; p53; therapy resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
miR-644a Inhibits Cellular Proliferation and Invasion via Suppression of CtBP1 in Gastric Cancer Cells.Oncol Res. 2018 Jan 19;26(1):1-8. doi: 10.3727/096504016X14772410356982. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Oncol Res. 2018. PMID: 27983935 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA485-3p negatively regulates the transcriptional co-repressor CtBP1 to control the oncogenic process in osteosarcoma cells.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Aug 6;14(11):1445-1456. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.26335. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30262996 Free PMC article.
-
miR-137 suppresses the invasion and procedure of EMT of human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 through targeting CtBP1.Hum Cell. 2016 Jan;29(1):30-6. doi: 10.1007/s13577-015-0124-4. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Hum Cell. 2016. PMID: 26337822
-
The Role of CtBP1 in Oncogenic Processes and Its Potential as a Therapeutic Target.Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Jun;16(6):981-990. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0592. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28576945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the multifaceted roles of long non-coding RNA CTBP1-DT in human diseases: Special attention to its microprotein-encoding potential.Pathol Res Pract. 2025 Apr;268:155870. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2025.155870. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Pathol Res Pract. 2025. PMID: 40020329 Review.
Cited by
-
HMGA2 promotes cancer metastasis by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 1;14:1320887. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1320887. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38361784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional miRNAs in breast cancer drug resistance.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Mar 19;11:1529-1541. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S152462. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29593419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-644a promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by downregulating the expression of heat shock factor 1.Cell Commun Signal. 2018 Jun 14;16(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12964-018-0244-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2018. PMID: 29898735 Free PMC article.
-
The CtBP1-HDAC1/2-IRF1 transcriptional complex represses the expression of the long noncoding RNA GAS5 in human osteosarcoma cells.Int J Biol Sci. 2019 Jun 2;15(7):1460-1471. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.33529. eCollection 2019. Int J Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31337976 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9: Transcending the Reality of Genome Editing.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017 Jun 16;7:211-222. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 Apr 8. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017. PMID: 28624197 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406:747–752. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. microRNAs: tiny regulators with great potential. Cell. 2001;107:823–826. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

