CCL2/CCR2 axis is associated with postoperative survival and recurrence of patients with non-metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 27409666
- PMCID: PMC5239494
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10492
CCL2/CCR2 axis is associated with postoperative survival and recurrence of patients with non-metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Chemokine (C-Cmotif) ligand 2 (CCL2) is a major chemokine that recruit monocytes and macrophages to the sites of inflammation. Recent researches have clarified that overexpression of CCL2 is associated with unfavorable prognosis in various cancer types. In this study, we aim to determine the prognostic value of CCL2 expression as well as its receptor C-C motif receptor type 2 (CCR2) in patients with non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) after surgery.
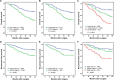
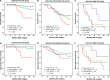
Results: Both high CCL2 and CCR2 expression were remarkably correlated with shortened survival time (P < 0.001 and P < 0.001, respectively) and increased risk of recurrence (P = 0.001 and P = 0.003, respectively). The combination of CCL2 and CCR2 expression (CCL2/CCR2 signature) could offer a better prognostic stratification. Furthermore, multivariate analyses identified CCL2/CCR2 signature as an independent risk factor for overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) (P = 0.007 and P = 0.043, respectively). The incorporation of CCL2/CCR2 signature would refine individual risk stratification and predictive accuracy of the well-established models.
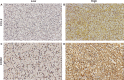
Materials and methods: We retrospectively examined the intratumoral expression of CCL2 and CCR2 by immunohistochemical staining in 268 histologically proven non-metastatic ccRCC patients receiving surgery in a single institution between 2001 and 2004. Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox regression were applied to determine the prognostic value of CCL2 and CCR2 expression. Concordance index was calculated to compare predictive accuracy of the established models.
Conclusions: Combined CCL2 and CCR2 expression emerges as an independent prognostic factor for non-metastatic ccRCC patients after surgical treatment.
Keywords: CCL2; CCR2; clear-cell renal cell carcinoma; overall survival; prognostic biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High expression of chemokine CCL2 is associated with recurrence after surgery in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.Urol Oncol. 2016 May;34(5):238.e19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2015.11.026. Epub 2015 Dec 31. Urol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26749463
-
High expression of Mucin13 associates with grimmer postoperative prognosis of patients with non-metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):7548-7558. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13692. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27911274 Free PMC article.
-
Low CCL17 expression associates with unfavorable postoperative prognosis of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2017 Feb 8;17(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3106-y. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28178948 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic tissuemarkers in clear cell and papillary renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Biomark. 2010;7(6):261-8. doi: 10.3233/CBM-2010-0195. Cancer Biomark. 2010. PMID: 21694464 Review.
-
Does chromophobe renal cell carcinoma have better survival than clear cell renal cell carcinoma? A clinical-based cohort study and meta-analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2016 Feb;48(2):191-9. doi: 10.1007/s11255-015-1161-3. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26589610 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-proliferative and anti-migratory properties of coffee diterpenes kahweol acetate and cafestol in human renal cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 12;11(1):675. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80302-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33436830 Free PMC article.
-
Is the C-C Motif Ligand 2-C-C Chemokine Receptor 2 Axis a Promising Target for Cancer Therapy and Diagnosis?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 7;21(23):9328. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239328. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33297571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CCL20-CCR6 Axis in Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 22;21(15):5186. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155186. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32707869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recruitment and Expansion of Tregs Cells in the Tumor Environment-How to Target Them?Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 13;13(8):1850. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081850. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33924428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CCL2 promotes EGFR-TKIs resistance in non-small cell lung cancer via the AKT-EMT pathway.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Jul 3;56(10):1549-1560. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024106. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 38961814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gupta K, Miller JD, Li JZ, Russell MW, Charbonneau C. Epidemiologic and socioeconomic burden of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC): a literature review. Cancer Treat Rev. 2008;34:193–205. - PubMed
-
- Ljungberg B, Bensalah K, Canfield S, Dabestani S, Hofmann F, Hora M, Kuczyk MA, Lam T, Marconi L, Merseburger AS, Mulders P, Powles T, Staehler M, et al. EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: 2014 update. Eur Urol. 2015;67:913–924. - PubMed
-
- Ljungberg B, Campbell SC, Choi HY, Jacqmin D, Lee JE, Weikert S, Kiemeney LA. The epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2011;60:615–621. - PubMed
-
- Sun M, Shariat SF, Cheng C, Ficarra V, Murai M, Oudard S, Pantuck AJ, Zigeuner R, Karakiewicz PI. Prognostic factors and predictive models in renal cell carcinoma: a contemporary review. Eur Urol. 2011;60:644–661. - PubMed
-
- Eichelberg C, Junker K, Ljungberg B, Moch H. Diagnostic and prognostic molecular markers for renal cell carcinoma: a critical appraisal of the current state of research and clinical applicability. Eur Urol. 2009;55:851–863. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

