Clinicopathological and Prognostic Value of Ki-67 Expression in Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 27410033
- PMCID: PMC4943634
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158891
Clinicopathological and Prognostic Value of Ki-67 Expression in Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Ki-67 is an established marker of cell proliferation, and the Ki-67 index correlates with the clinical course of several cancer types, including bladder cancer (BC). However, the clinicopathological and prognostic significance of Ki-67 in bladder cancer remains unclear. Therefore, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to clarify this relationship.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search for relevant studies published up to February 1, 2016, was performed using PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase and ISI Web of Knowledge. The effects of Ki-67 expression on survival outcome in patients with BC and BC subtypes were evaluated. Furthermore, the relationship between Ki-67 expression and the clinicopathological features of BC were assessed.
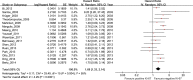
Results: Thirty-one studies with 5147 bladder cancer patients were selected for evaluation. Ki-67 expression was significantly associated with shorter recurrence-free (HR 1.69, 95% CI: 1.33-2.14), progression-free (HR 1.89, 95% CI: 1.43-2.51), overall (HR 2.03, 95% CI: 1.31-3.16), and cancer-specific (HR 1.69, 95% CI: 1.47-1.95) survival. Moreover, whereas high expression was more common in high tumor stage, recurrence status, tumor size, there was no correlation between high Ki-67 expression and age, gender, smoking habits, and tumor number. Importantly, analysis of the different subgroups of BC suggested that significant correlations between high Ki-67 expression and survival outcome (recurrence-free/progression-free/overall/cancer-specific survival) are present only in European-American patients.
Conclusion: The present results indicate that over-expression of Ki-67 is distinctly correlated with poor patient survival. Ki-67 may serve as a valuable biomarker for prognosis in BC patients, particularly in non-Asian BC patients. The results suggest no significant association between Ki-67 expression and BC prognosis in Asian patients. Further efforts are needed to fully clarify this relationship.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of different cut-off levels of Ki-67 in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 64,196 patients.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Oct;153(3):477-91. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3559-0. Epub 2015 Sep 4. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 26341751
-
Treatment options for progression or recurrence of glioblastoma: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 4;5(1):CD013579. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013579.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34559423 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
URINARY BLADDER CANCER RECURRENCE AND EXPRESSION OF LYNCH AND HER MARKERS: SEARCHING FOR IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL PATTERNS AMONG 113 TUMORS FROM 33 PATIENTS.Acta Clin Croat. 2022 Aug;61(2):239-247. doi: 10.20471/acc.2022.61.02.10. Acta Clin Croat. 2022. PMID: 36818940 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic role of Ki-67/MIB-1 in meningioma: A systematic review with meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Feb;99(9):e18644. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018644. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32118704 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Safety and Versatility of 4D Printed Intravesical Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 24;15(3):757. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030757. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986618 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Ki-67 as Predictive Biomarkers Identify Patients Who Will Be More Sensitive to Intravesical Instillations for the Prevention of Bladder Cancer Recurrence after Radical Nephroureterectomy.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 21;11(11):e0166884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166884. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27870887 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic and prognostic values of Ki-67/MIB-1 expression in thyroid cancer: a meta-analysis with 6,051 cases.Onco Targets Ther. 2017 Jul 3;10:3261-3276. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S135593. eCollection 2017. Onco Targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 28740401 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

