Ipilimumab for Patients with Relapse after Allogeneic Transplantation
- PMID: 27410923
- PMCID: PMC5149459
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1601202
Ipilimumab for Patients with Relapse after Allogeneic Transplantation
Abstract
Background: Loss of donor-mediated immune antitumor activity after allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) permits relapse of hematologic cancers. We hypothesized that immune checkpoint blockade established by targeting cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 with ipilimumab could restore antitumor reactivity through a graft-versus-tumor effect.
Methods: We conducted a phase 1/1b multicenter, investigator-initiated study to determine the safety and efficacy of ipilimumab in patients with relapsed hematologic cancer after allogeneic HSCT. Patients received induction therapy with ipilimumab at a dose of 3 or 10 mg per kilogram of body weight every 3 weeks for a total of 4 doses, with additional doses every 12 weeks for up to 60 weeks in patients who had a clinical benefit.
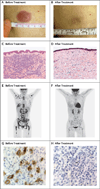
Results: A total of 28 patients were enrolled. Immune-related adverse events, including one death, were observed in 6 patients (21%), and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) that precluded further administration of ipilimumab was observed in 4 patients (14%). No responses that met formal response criteria occurred in patients who received a dose of 3 mg per kilogram. Among 22 patients who received a dose of 10 mg per kilogram, 5 (23%) had a complete response, 2 (9%) had a partial response, and 6 (27%) had decreased tumor burden. Complete responses occurred in 4 patients with extramedullary acute myeloid leukemia and 1 patient with the myelodysplastic syndrome developing into acute myeloid leukemia. Four patients had a durable response for more than 1 year. Responses were associated with in situ infiltration of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, decreased activation of regulatory T cells, and expansion of subpopulations of effector T cells in the blood.
Conclusions: Our early-phase data showed that administration of ipilimumab was feasible in patients with recurrent hematologic cancers after allogeneic HSCT, although immune-mediated toxic effects and GVHD occurred. Durable responses were observed in association with several histologic subtypes of these cancers, including extramedullary acute myeloid leukemia. (Funded by the National Institutes of Health and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01822509.).
Figures


Comment in
-
Haematological cancer: CTLA-4 blockade after allo-SCT.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016 Sep;13(9):530. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.124. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27480666 No abstract available.
References
-
- Antin JH. Graft-versus-leukemia: no longer an epiphenomenon. Blood. 1993;82:2273–2277. - PubMed
-
- Alyea EP, Kim HT, Ho V, et al. Comparative outcome of nonmyeloablative and myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for patients older than 50 years of age. Blood. 2005;105:1810–1814. - PubMed
-
- Mielcarek M, Storer BE, Flowers ME, Storb R, Sandmaier BM, Martin PJ. Outcomes among patients with recurrent high-risk hematologic malignancies after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007;13:1160–1168. - PubMed
-
- Soiffer RJ. Donor lymphocyte infusions for acute myeloid leukaemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2008;21:455–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
