Tissue-Engineered Vascular Rings from Human iPSC-Derived Smooth Muscle Cells
- PMID: 27411102
- PMCID: PMC4945325
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.05.004
Tissue-Engineered Vascular Rings from Human iPSC-Derived Smooth Muscle Cells
Abstract
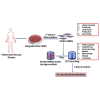
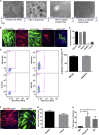
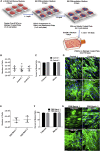
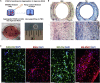
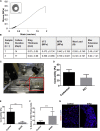
There is an urgent need for an efficient approach to obtain a large-scale and renewable source of functional human vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) to establish robust, patient-specific tissue model systems for studying the pathogenesis of vascular disease, and for developing novel therapeutic interventions. Here, we have derived a large quantity of highly enriched functional VSMCs from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC-VSMCs). Furthermore, we have engineered 3D tissue rings from hiPSC-VSMCs using a facile one-step cellular self-assembly approach. The tissue rings are mechanically robust and can be used for vascular tissue engineering and disease modeling of supravalvular aortic stenosis syndrome. Our method may serve as a model system, extendable to study other vascular proliferative diseases for drug screening. Thus, this report describes an exciting platform technology with broad utility for manufacturing cell-based tissues and materials for various biomedical applications.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Xenogeneic-free generation of vascular smooth muscle cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells for vascular tissue engineering.Acta Biomater. 2021 Jan 1;119:155-168. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.10.042. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33130306 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular smooth muscle cells derived from inbred swine induced pluripotent stem cells for vascular tissue engineering.Biomaterials. 2017 Dec;147:116-132. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.09.019. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Biomaterials. 2017. PMID: 28942128 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced elastin synthesis and maturation in human vascular smooth muscle tissue derived from induced-pluripotent stem cells.Acta Biomater. 2017 Apr 1;52:49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.01.083. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28163239
-
Differentiation and Application of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Nov;37(11):2026-2037. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309196. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28860223 Review.
-
Generation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells From Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells: Methods, Applications, and Considerations.Circ Res. 2021 Mar 5;128(5):670-686. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.318049. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Circ Res. 2021. PMID: 33818124 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modular design of a tissue engineered pulsatile conduit using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.Acta Biomater. 2020 Jan 15;102:220-230. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.10.019. Epub 2019 Oct 19. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 31634626 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of Tissue-Engineered Blood Vessels with Spatially Controlled Heterogeneities.Tissue Eng Part A. 2018 Oct;24(19-20):1492-1503. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2017.0492. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018. PMID: 29724157 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-Engineered Vascular Grafts with Advanced Mechanical Strength from Human iPSCs.Cell Stem Cell. 2020 Feb 6;26(2):251-261.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.12.012. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Cell Stem Cell. 2020. PMID: 31956039 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling human diseases with induced pluripotent stem cells: from 2D to 3D and beyond.Development. 2018 Mar 8;145(5):dev156166. doi: 10.1242/dev.156166. Development. 2018. PMID: 29519889 Free PMC article.
-
Serum-Free Manufacturing of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Tissue Rings Using Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Stem Cells Int. 2019 Jan 15;2019:5654324. doi: 10.1155/2019/5654324. eCollection 2019. Stem Cells Int. 2019. PMID: 30766604 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

