NOS Expression and NO Function in Glioma and Implications for Patient Therapies
- PMID: 27411305
- PMCID: PMC5467121
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2016.6820
NOS Expression and NO Function in Glioma and Implications for Patient Therapies
Abstract
Significance: Gliomas are central nervous system tumors that primarily occur in the brain and arise from glial cells. Gliomas include the most common malignant brain tumor in adults known as grade IV astrocytoma, or glioblastoma (GBM). GBM is a deadly disease for which the most significant advances in treatment offer an improvement in survival of only ∼2 months.
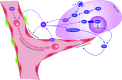
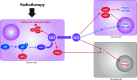
Critical issues: To develop novel treatments and improve patient outcomes, we and others have sought to determine the role of molecular signals in gliomas. Recent Advances: One signaling molecule that mediates important biologies in glioma is the free radical nitric oxide (NO). In glioma cells and the tumor microenvironment, NO is produced by three isoforms of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), NOS1, NOS2, and NOS3. NO and NOS affect glioma growth, invasion, angiogenesis, immunosuppression, differentiation state, and therapeutic resistance.
Future directions: These multifaceted effects of NO and NOS on gliomas both in vitro and in vivo suggest the potential of modulating the pathway for antiglioma patient therapies. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 26, 986-999.
Keywords: cancer stem cell; glioma; nitric oxide synthase/NOS; nitric oxide/NO; therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The implications of nitric oxide metabolism in the treatment of glial tumors.Neurochem Int. 2021 Nov;150:105172. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105172. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Neurochem Int. 2021. PMID: 34461111 Review.
-
Lipopolysaccharide plus 12-o-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate induction of migration and invasion of glioma cells in vitro and in vivo: Differential inhibitory effects of flavonoids.Neuroscience. 2006 Jun 30;140(2):477-89. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.02.028. Epub 2006 Apr 3. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16580779
-
Nitric oxide and glioma: a target for novel therapy?Br J Neurosurg. 2001 Jun;15(3):213-20. doi: 10.1080/02688690120057628. Br J Neurosurg. 2001. PMID: 11478055 Review.
-
Adrenomedullin and nitric oxide: implications for the etiology and treatment of primary brain tumors.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011 Nov;10(7):820-33. doi: 10.2174/187152711798072374. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21999731 Review.
-
Increased brain tumor microvessel permeability after intracarotid bradykinin infusion is mediated by nitric oxide.Cancer Res. 1996 Sep 1;56(17):4027-31. Cancer Res. 1996. PMID: 8752174
Cited by
-
Glioma and microglia, a double entendre.Nat Immunol. 2016 Oct 19;17(11):1240-1242. doi: 10.1038/ni.3586. Nat Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27760107 No abstract available.
-
Nitric Oxide Antagonism to Anti-Glioblastoma Photodynamic Therapy: Mitigation by Inhibitors of Nitric Oxide Generation.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Feb 15;11(2):231. doi: 10.3390/cancers11020231. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30781428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitroproteomics is instrumental for stratification and targeted treatments of astrocytoma patients: expert recommendations for advanced 3PM approach with improved individual outcomes.EPMA J. 2023 Dec 6;14(4):673-696. doi: 10.1007/s13167-023-00348-y. eCollection 2023 Dec. EPMA J. 2023. PMID: 38094577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated omics characterization reveals reduced cancer indicators and elevated inflammatory factors after thermal ablation in non-small cell lung cancer patients.Respir Res. 2024 Aug 14;25(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02917-9. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39143582 Free PMC article.
-
Negative effects of tumor cell nitric oxide on anti-glioblastoma photodynamic therapy.J Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2020;6:52. doi: 10.20517/2394-4722.2020.107. Epub 2020 Dec 24. J Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2020. PMID: 33564720 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Badn W, Hegardt P, Fellert MA, Darabi A, Esbjornsson M, Smith KE, Janelidze S, Salford LG, Visse E, and Siesjo P. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase enhances anti-tumour immune responses in rats immunized with IFN-gamma-secreting glioma cells. Scand J Immunol 65: 289–297, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Badn W, Visse E, Darabi A, Smith KE, Salford LG, and Siesjo P. Postimmunization with IFN-gamma-secreting glioma cells combined with the inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor mercaptoethylguanidine prolongs survival of rats with intracerebral tumors. J Immunol 179: 4231–4238, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Bakshi A, Nag TC, Wadhwa S, Mahapatra AK, and Sarkar C. The expression of nitric oxide synthases in human brain tumours and peritumoral areas. J Neurol Sci 155: 196–203, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD, and Rich JN. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444: 756–760, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Wu Q, Sathornsumetee S, Hao Y, Li Z, Hjelmeland AB, Shi Q, McLendon RE, Bigner DD, and Rich JN. Stem cell-like glioma cells promote tumor angiogenesis through vascular endothelial growth factor. Cancer Res 66: 7843–7848, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

