Anti-allodynic effect of intrathecal processed Aconitum jaluense is associated with the inhibition of microglial activation and P2X7 receptor expression in spinal cord
- PMID: 27411500
- PMCID: PMC4944236
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1201-2
Anti-allodynic effect of intrathecal processed Aconitum jaluense is associated with the inhibition of microglial activation and P2X7 receptor expression in spinal cord
Abstract
Background: For their analgesic and anti-arthritic effects, Aconitum species have been used in folk medicine in some East Asian countries. Although their analgesic effect is attributed to its action on voltage-dependent sodium channels, they also suppress purinergic receptor expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons in rats with neuropathic pain. In vitro study also demonstrated that the Aconitum suppresses ATP-induced P2X7 receptor (P2X7R)-mediated inflammatory responses in microglial cell lines. Herein, we examined the effect of intrathecal administration of thermally processed Aconitum jaluense (PA) on pain behavior, P2X7R expression and microglial activation in a rat spinal nerve ligation (SNL) model.
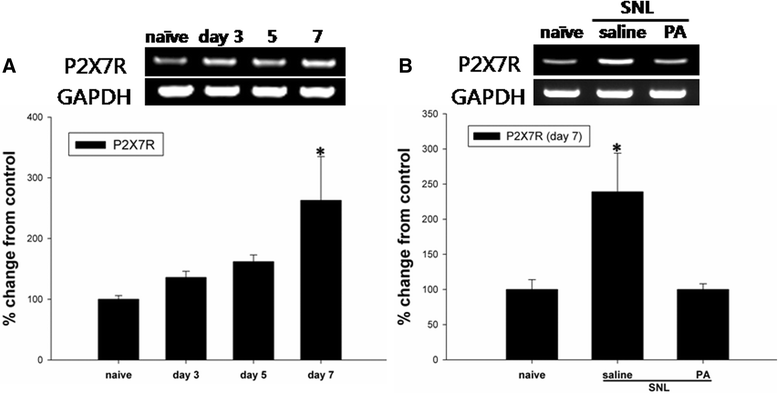
Methods: Mechanical allodynia induced by L5 SNL in Sprague-Dawley rats was measured using the von Frey test to evaluate the effect of intrathecal injection of PA. Changes in the expression of P2X7R in the spinal cord were examined using RT-PCR and Western blot analysis. In addition, the effect of intrathecal PA on microglial activation was evaluated by immunofluorescence.
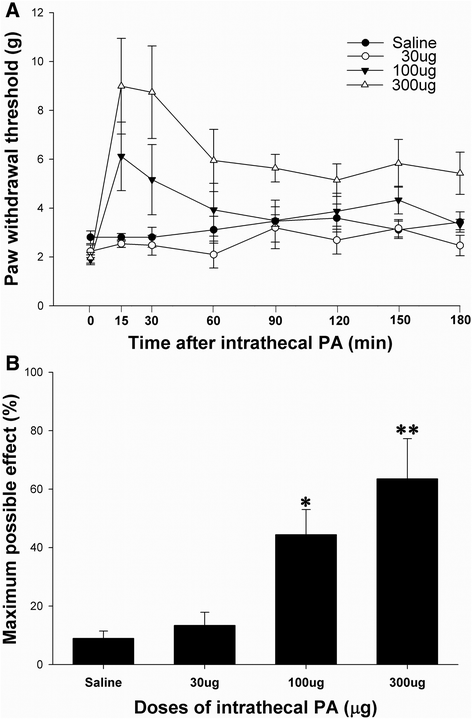
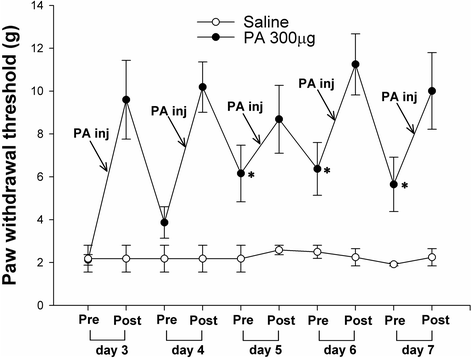
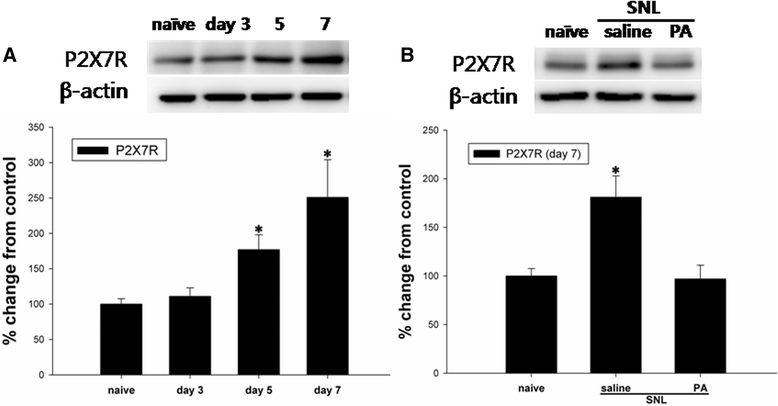
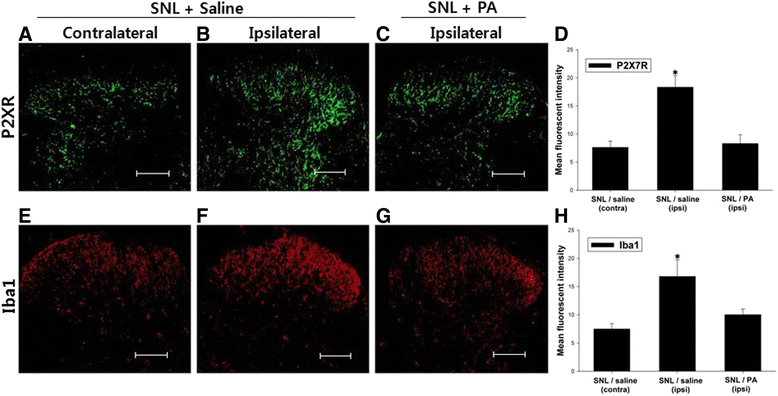
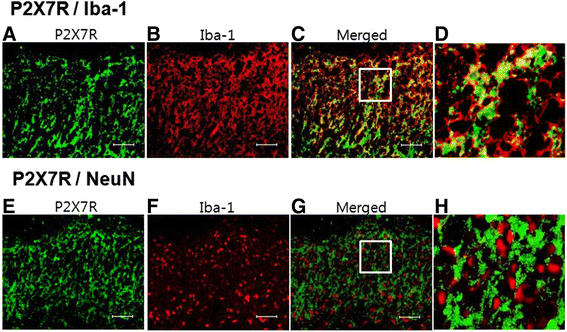
Results: Intrathecal PA attenuated mechanical allodynia in a dose-dependent manner showing both acute and chronic effects with 65 % of the maximal possible effect. The expression and production of spinal P2X7R was increased five days after SNL, but daily intrathecal PA injection significantly inhibited the increase to the level of naïve animals. Immunofluorescence of the spinal cord revealed a significant increase in P2X7R expression and activation of microglia in the dorsal horn, which was inhibited by intrathecal PA treatment. P2X7R co-localized with microglia marker, but not neurons.
Conclusions: Intrathecal PA exerts anti-allodynic effects in neuropathic pain, possibly by suppressing P2X7R production and expression as well as reducing microglial activation in the spinal cord.
Keywords: Aconitum jaluense; Allodynia; Microglia; P2X7 receptor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pre-emptive intrathecal quinidine alleviates spinal nerve ligation-induced peripheral neuropathic pain.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 Aug;63(8):1063-9. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01318.x. Epub 2011 Jun 11. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21718290
-
Involvement of microglial P2X7 receptors and downstream signaling pathways in long-term potentiation of spinal nociceptive responses.Brain Behav Immun. 2010 Oct;24(7):1176-89. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.06.001. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Brain Behav Immun. 2010. PMID: 20554014
-
Effects of riluzole on P2X7R expression in the spinal cord in rat model of neuropathic pain.Neurosci Lett. 2016 Apr 8;618:127-133. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.02.065. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Neurosci Lett. 2016. PMID: 26952972
-
Roles of purinergic P2X7 receptor in glioma and microglia in brain tumors.Cancer Lett. 2017 Aug 28;402:93-99. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 May 20. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28536012 Review.
-
Involvement of microglial P2X7 receptor in pain modulation.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Jan;30(1):e14496. doi: 10.1111/cns.14496. Epub 2023 Nov 10. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37950524 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dissecting the Underlying Pharmaceutical Mechanism of Chinese Traditional Medicine Yun-Pi-Yi-Shen-Tong-Du-Tang Acting on Ankylosing Spondylitis through Systems Biology Approaches.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 18;7(1):13436. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13723-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29044146 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture may alleviate neuropathic pain via suppressing P2X7R expression.Mol Pain. 2021 Jan-Dec;17:1744806921997654. doi: 10.1177/1744806921997654. Mol Pain. 2021. PMID: 33626989 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the P2X7 receptor in midbrain periaqueductal gray participates in the analgesic effect of tramadol in bone cancer pain rats.Mol Pain. 2018 Jan-Dec;14:1744806918803039. doi: 10.1177/1744806918803039. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Mol Pain. 2018. PMID: 30198382 Free PMC article.
-
PRG-1 relieves pain and depressive-like behaviors in rats of bone cancer pain by regulation of dendritic spine in hippocampus.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Sep 21;17(14):4005-4020. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.59032. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34671215 Free PMC article.
-
Intrathecal administration of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells genetically modified with human proenkephalin gene decrease nociceptive pain in neuropathic rats.Mol Pain. 2017 Jan;13:1744806917701445. doi: 10.1177/1744806917701445. Mol Pain. 2017. PMID: 28326940 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

