1-methylnicotinamide and its structural analog 1,4-dimethylpyridine for the prevention of cancer metastasis
- PMID: 27412454
- PMCID: PMC4944260
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-016-0389-9
1-methylnicotinamide and its structural analog 1,4-dimethylpyridine for the prevention of cancer metastasis
Abstract
Background: 1-methylnicotinamide (1-MNA), an endogenous metabolite of nicotinamide, has recently gained interest due to its anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombotic activities linked to the COX-2/PGI2 pathway. Given the previously reported anti-metastatic activity of prostacyclin (PGI2), we aimed to assess the effects of 1-MNA and its structurally related analog, 1,4-dimethylpyridine (1,4-DMP), in the prevention of cancer metastasis.
Methods: All the studies on the anti-tumor and anti-metastatic activity of 1-MNA and 1,4-DMP were conducted using the model of murine mammary gland cancer (4T1) transplanted either orthotopically or intravenously into female BALB/c mouse. Additionally, the effect of the investigated molecules on cancer cell-induced angiogenesis was estimated using the matrigel plug assay utilizing 4T1 cells as a source of pro-angiogenic factors.
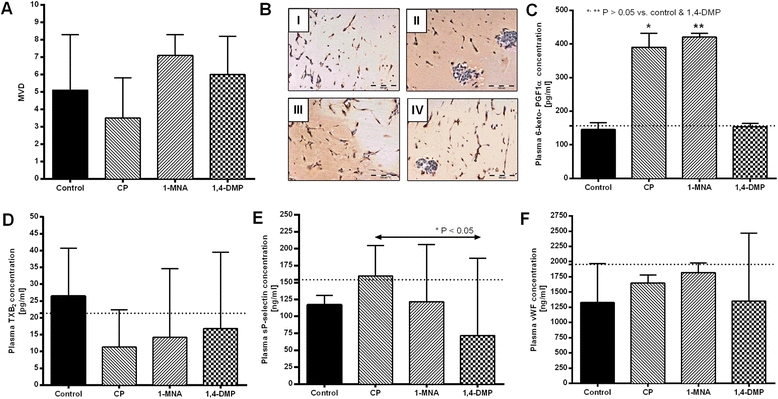
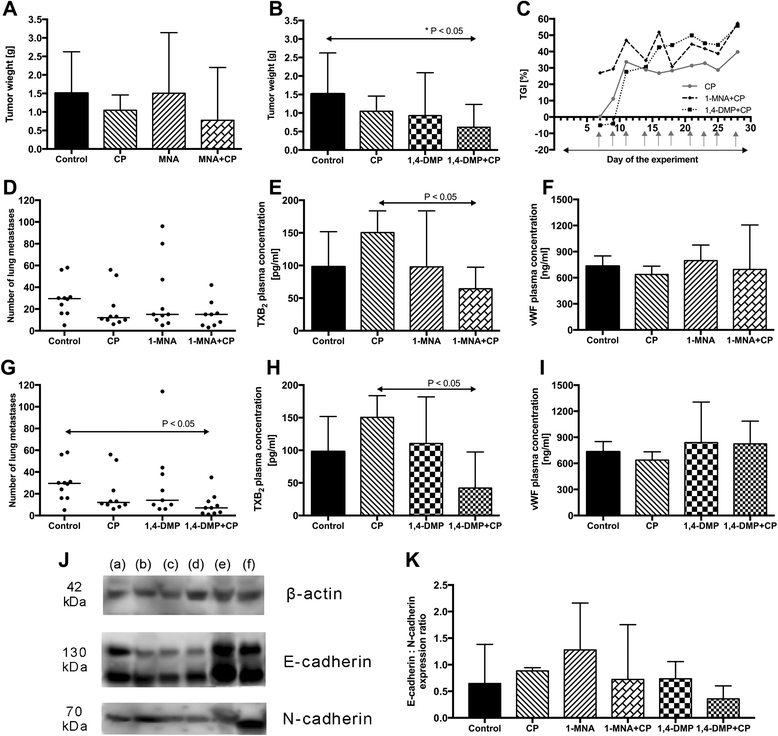
Results: Neither 1-MNA nor 1,4-DMP, when given in a monotherapy of metastatic cancer, influenced the growth of 4T1 primary tumors transplanted orthotopically; however, both compounds tended to inhibit 4T1 metastases formation in lungs of mice that were orthotopically or intravenously inoculated with 4T1 or 4T1-luc2-tdTomato cells, respectively. Additionally, while 1-MNA enhanced tumor vasculature formation and markedly increased PGI2 generation, 1,4-DMP did not have such an effect. The anti-metastatic activity of 1-MNA and 1,4-DMP was further confirmed when both agents were applied with a cytostatic drug in a combined treatment of 4T1 murine mammary gland cancer what resulted in up to 80 % diminution of lung metastases formation.
Conclusions: The results of the studies presented below indicate that 1-MNA and its structural analog 1,4-DMP prevent metastasis and might be beneficially implemented into the treatment of metastatic breast cancer to ensure a comprehensive strategy of metastasis control.
Keywords: 1,4-dimethylpyridinium chloride; 1-methylnicotinaimide chloride; Angiogenesis; Breast cancer; Combined therapy; Metastasis.
Figures


References
-
- Pozzi V, Sartini D, Morganti S, Giuliante R, Di Ruscio G, Santarelli A, Rocchetti R, Rubini C, Tomasetti M, Giannatempo G, et al. RNA-mediated gene silencing of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase is associated with decreased tumorigenicity in human oral carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 2013;8:e71272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071272. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

