Monosialoganglioside-Containing Nanoliposomes Restore Endothelial Function Impaired by AL Amyloidosis Light Chain Proteins
- PMID: 27412900
- PMCID: PMC4937272
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003318
Monosialoganglioside-Containing Nanoliposomes Restore Endothelial Function Impaired by AL Amyloidosis Light Chain Proteins
Abstract
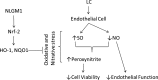
Background: Light chain amyloidosis (AL) is associated with high mortality, especially in patients with advanced cardiovascular involvement. It is caused by toxicity of misfolded light chain proteins (LC) in vascular, cardiac, and other tissues. There is no treatment to reverse LC tissue toxicity. We tested the hypothesis that nanoliposomes composed of monosialoganglioside, phosphatidylcholine, and cholesterol (GM1 ganglioside-containing nanoliposomes [NLGM1]) can protect against LC-induced human microvascular dysfunction and assess mechanisms behind the protective effect.
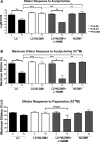
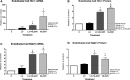
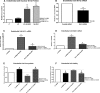
Methods and results: The dilator responses of ex vivo abdominal adipose arterioles from human participants without AL to acetylcholine and papaverine were measured before and after exposure to LC (20 μg/mL) with or without NLGM1 (1:10 ratio for LC:NLGM1 mass). Human umbilical vein endothelial cells were exposed for 18 to 20 hours to vehicle, LC with or without NLGM1, or NLGM1 and compared for oxidative and nitrative stress response and cellular viability. LC impaired arteriole dilator response to acetylcholine, which was restored by co-treatment with NLGM1. LC decreased endothelial cell nitric oxide production and cell viability while increasing superoxide and peroxynitrite; these adverse effects were reversed by NLGM1. NLGM1 increased endothelial cell protein expression of antioxidant enzymes heme oxygenase 1 and NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 and increased nuclear factor, erythroid 2 like 2 (Nrf-2) protein. Nrf-2 gene knockdown reduced antioxidant stress response and reversed the protective effects of NLGM1.
Conclusions: NLGM1 protects against LC-induced human microvascular endothelial dysfunction through increased nitric oxide bioavailability and reduced oxidative and nitrative stress mediated by Nrf-2-dependent antioxidant stress response. These findings point to a potential novel therapeutic approach for light chain amyloidosis.
Keywords: amyloid; endothelium; nanotechnology; oxidant stress.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures
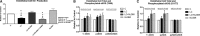
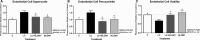
Similar articles
-
PEGylated-nanoliposomal clusterin for amyloidogenic light chain-induced endothelial dysfunction.J Liposome Res. 2018 Jun;28(2):97-105. doi: 10.1080/08982104.2016.1274756. Epub 2017 Feb 10. J Liposome Res. 2018. PMID: 28103719 Free PMC article.
-
Human microvascular dysfunction and apoptotic injury induced by AL amyloidosis light chain proteins.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Dec;301(6):H2305-12. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00503.2011. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21963839 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoliposomes protect against human arteriole endothelial dysfunction induced by β-amyloid peptide.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016 Feb;36(2):405-12. doi: 10.1177/0271678X15610134. Epub 2015 Oct 8. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016. PMID: 26661197 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress, nitric oxide, and vascular disease.J Card Surg. 2002 Jul-Aug;17(4):324-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8191.2001.tb01151.x. J Card Surg. 2002. PMID: 12546080 Review.
-
Research progress on toxicity, function, and mechanism of metal oxide nanoparticles on vascular endothelial cells.J Appl Toxicol. 2021 May;41(5):683-700. doi: 10.1002/jat.4121. Epub 2020 Nov 26. J Appl Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33244813 Review.
Cited by
-
Multimodality Imaging Reveals Divergent Responses of Left and Right Heart to Treatment in Cardiac Amyloidosis.JACC Case Rep. 2019 Oct 16;1(3):360-366. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2019.07.034. eCollection 2019 Oct. JACC Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 34316826 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloidogenic medin induces endothelial dysfunction and vascular inflammation through the receptor for advanced glycation endproducts.Cardiovasc Res. 2017 Sep 1;113(11):1389-1402. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx135. Cardiovasc Res. 2017. PMID: 28859297 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Immune Activation by Medin: Potential Role in Cerebrovascular Disease and Reversal by Monosialoganglioside-Containing Nanoliposomes.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jan 21;9(2):e014810. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.014810. Epub 2020 Jan 13. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 31928157 Free PMC article.
-
PEGylated-nanoliposomal clusterin for amyloidogenic light chain-induced endothelial dysfunction.J Liposome Res. 2018 Jun;28(2):97-105. doi: 10.1080/08982104.2016.1274756. Epub 2017 Feb 10. J Liposome Res. 2018. PMID: 28103719 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Therapeutic Nanomaterials: Applications in Biology and Medicine.Mater Today (Kidlington). 2023 Jan-Feb;62:190-224. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2022.11.007. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Mater Today (Kidlington). 2023. PMID: 36938366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Falk RH. Diagnosis and management of the cardiac amyloidoses. Circulation. 2005;112:2047–2060. - PubMed
-
- Dubrey S, Mendes L, Skinner M, Falk RH. Resolution of heart failure in patients with AL amyloidosis. Ann Intern Med. 1996;125:481–484. - PubMed
-
- Kyle RA, Wagoner RD, Holley KE. Primary systemic amyloidosis: resolution of the nephrotic syndrome with melphalan and prednisone. Arch Intern Med. 1982;142:1445–1447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

