Effect of Toll-Like Receptor 4 on Synovial Injury of Temporomandibular Joint in Rats Caused by Occlusal Interference
- PMID: 27413256
- PMCID: PMC4931072
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/7694921
Effect of Toll-Like Receptor 4 on Synovial Injury of Temporomandibular Joint in Rats Caused by Occlusal Interference
Abstract
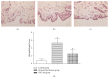
Synovitis is an important disease that causes intractable pain in TMJ. Some investigations suggested that the increasing expression of IL-1β secreted by synovial lining cells plays an important role in synovial inflammation and cartilage destruction in TMJ. In our previous research, the results demonstrated that TLR4 is involved in the expression of IL-1β in SFs from TMJ with lipopolysaccharide stimulation. However, the inflammatory response that occurred in synovial membrane is not caused by bacterial infection. In the current study, we investigated whether or not TLR4 participates in the inflammatory responses and the expression of IL-1β in synovial membrane of rats induced by occlusal interference. The results showed that obvious inflammation changes were observed in the synovial membranes and the expression of TLR4 and IL-1β was increased at both mRNA and protein levels in the occlusal interference rats. In addition, the inflammation reactions and the increased expression of IL-1β could be restrained by treatment with TAK-242, a blocker of TLR4 signaling. The results prompted us that the activation of TLR4 may be involved in the inflammatory reactions and increased expression of IL-1β in patients with synovitis and participate in the mechanisms of the initiation and development of synovial injury by regulating the expression of inflammatory mediators like IL-1β in synovial membranes.
Figures


References
-
- ĆElić R., Braut V., Petričević N. Influence of depression and somatization on acute and chronic orofacial pain in patients with single or multiple TMD diagnoses. Collegium Antropologicum. 2011;35(3):709–713. - PubMed
-
- Manfredini D., Guarda-Nardini L., Winocur E., Piccotti F., Ahlberg J., Lobbezoo F. Research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders: a systematic review of axis I epidemiologic findings. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontology. 2011;112(4):453–462. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2011.04.021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Suvinen T. I., Reade P. C., Kemppainen P., Könönen M., Dworkin S. F. Review of aetiological concepts of temporomandibular pain disorders: towards a biopsychosocial model for integration of physical disorder factors with psychological and psychosocial illness impact factors. European Journal of Pain. 2005;9(6):613–633. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2005.01.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Raustia A. M., Pirttiniemi P. M., Pyhtinen J. Correlation of occlusal factors and condyle position asymmetry with signs and symptoms of temporomandibular disorders in young adults. Cranio: The Journal of Craniomandibular Practice. 1995;13(3):152–156. - PubMed
-
- Sato H., Fujii T., Kitamori H. The clinical significance of the horizontal condylar angle in patients with temporomandibular disorders. Cranio. 1997;15(3):229–235. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

