T- and B-cell responses to multivalent prime-boost DNA and viral vectored vaccine combinations against hepatitis C virus in non-human primates
- PMID: 27416077
- PMCID: PMC7091906
- DOI: 10.1038/gt.2016.55
T- and B-cell responses to multivalent prime-boost DNA and viral vectored vaccine combinations against hepatitis C virus in non-human primates
Abstract
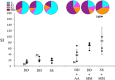
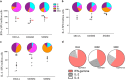
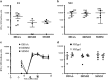
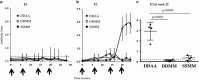
Immune responses against multiple epitopes are required for the prevention of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, and the progression to phase I trials of candidates may be guided by comparative immunogenicity studies in non-human primates. Four vectors, DNA, SFV, human serotype 5 adenovirus (HuAd5) and Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA) poxvirus, all expressing hepatitis C virus Core, E1, E2 and NS3, were combined in three prime-boost regimen, and their ability to elicit immune responses against HCV antigens in rhesus macaques was explored and compared. All combinations induced specific T-cell immune responses, including high IFN-γ production. The group immunized with the SFV+MVA regimen elicited higher E2-specific responses as compared with the two other modalities, while animals receiving HuAd5 injections elicited lower IL-4 responses as compared with those receiving MVA. The IFN-γ responses to NS3 were remarkably similar between groups. Only the adenovirus induced envelope-specific antibody responses, but these failed to show neutralizing activity. Therefore, the two novel regimens failed to induce superior responses as compared with already existing HCV vaccine candidates. Differences were found in response to envelope proteins, but the relevance of these remain uncertain given the surprisingly poor correlation with immunogenicity data in chimpanzees, underlining the difficulty to predict efficacy from immunology studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Forns X, Payette PJ, Ma X, Satterfield W, Eder G, Mushahwar IK. Vaccination of chimpanzees with plasmid DNA encoding the hepatitis C virus (HCV) envelope E2 protein modified the infection after challenge with homologous monoclonal HCV. Hepatology. 2000;32:618–625. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2000.9877. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rollier C, Depla E, Drexhage JA, Verschoor EJ, Verstrepen BE, Fatmi Control of heterologous hepatitis C virus infection in chimpanzees is associated with the quality of vaccine-induced peripheral T-helper immune response. J Virol. 2004;78:187–196. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.1.187-196.2004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

