Regulation and function of AMPK in physiology and diseases
- PMID: 27416781
- PMCID: PMC4973318
- DOI: 10.1038/emm.2016.81
Regulation and function of AMPK in physiology and diseases
Abstract
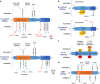
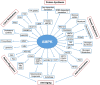
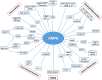
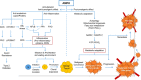
5'-adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is an evolutionarily conserved serine/threonine kinase that was originally identified as the key player in maintaining cellular energy homeostasis. Intensive research over the last decade has identified diverse molecular mechanisms and physiological conditions that regulate the AMPK activity. AMPK regulates diverse metabolic and physiological processes and is dysregulated in major chronic diseases, such as obesity, inflammation, diabetes and cancer. On the basis of its critical roles in physiology and pathology, AMPK is emerging as one of the most promising targets for both the prevention and treatment of these diseases. In this review, we discuss the current understanding of the molecular and physiological regulation of AMPK and its metabolic and physiological functions. In addition, we discuss the mechanisms underlying the versatile roles of AMPK in diabetes and cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Davies SP, Hawley SA, Woods A, Carling D, Haystead TA, Hardie DG. Purification of the AMP-activated protein kinase on ATP-gamma-sepharose and analysis of its subunit structure. Eur J Biochem 1994; 223: 351–357. - PubMed
-
- Voss M, Paterson J, Kelsall IR, Martin-Granados C, Hastie CJ, Peggie MW et al. Ppm1E is an in cellulo AMP-activated protein kinase phosphatase. Cell Signal 2011; 23: 114–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

