Structural and functional insights into IZUMO1 recognition by JUNO in mammalian fertilization
- PMID: 27416963
- PMCID: PMC4947182
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12198
Structural and functional insights into IZUMO1 recognition by JUNO in mammalian fertilization
Abstract
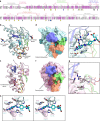
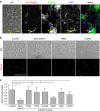
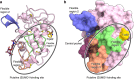
Sperm-egg fusion is the critical step in mammalian fertilization, and requires the interaction between IZUMO1 on the sperm surface and JUNO (also known as folate receptor (FR) 4 or IZUMO1R) on the egg surface. Whereas other FRs bind and uptake folates, JUNO binds IZUMO1 and establishes the cell-cell adhesion. However, the mechanism of IZUMO1 recognition by JUNO has remained elusive. Here we report the crystal structure of mouse JUNO, at 2.3 Å resolution. A structural comparison of JUNO with the FRs revealed that JUNO and the FRs have similar overall structures, but JUNO lacks the folate-binding pocket, thereby explaining the inability of JUNO to bind folate. Further complementation of Juno knockout eggs with mutant Juno messenger RNAs revealed that the conserved, surface-exposed tryptophan residue of JUNO is required for sperm binding and fertilization. Our structure-based in vivo functional analyses provide a framework towards a mechanistic understanding of mammalian gamete recognition.
Figures


References
-
- Inoue N., Ikawa M., Isotani A. & Okabe M. The immunoglobulin superfamily protein Izumo is required for sperm to fuse with eggs. Nature 434, 234–238 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Yanagimachi R., Yanagimachi H. & Rogers B. J. The use of zona-free animal ova as a test-system for the assessment of the fertilizing capacity of human spermatozoa. Biol. Reprod. 15, 471–476 (1976). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

