Identification of an ATP-controlled allosteric switch that controls actin filament nucleation by Arp2/3 complex
- PMID: 27417392
- PMCID: PMC4947185
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12226
Identification of an ATP-controlled allosteric switch that controls actin filament nucleation by Arp2/3 complex
Abstract
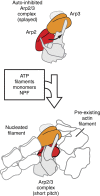
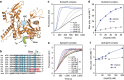
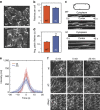
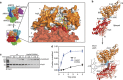
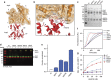
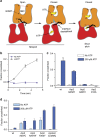
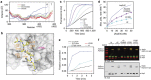
Nucleation of branched actin filaments by Arp2/3 complex is tightly regulated to control actin assembly in cells. Arp2/3 complex activation involves conformational changes brought about by ATP, Nucleation Promoting Factor (NPF) proteins, actin filaments and NPF-recruited actin monomers. To understand how these factors promote activation, we must first understand how the complex is held inactive in their absence. Here we demonstrate that the Arp3 C-terminal tail is a structural switch that prevents Arp2/3 complex from adopting an active conformation. The interaction between the tail and a hydrophobic groove in Arp3 blocks movement of Arp2 and Arp3 into an activated filament-like (short pitch) conformation. Our data indicate ATP binding destabilizes this interaction via an allosteric link between the Arp3 nucleotide cleft and the hydrophobic groove, thereby promoting the short-pitch conformation. Our results help explain how Arp2/3 complex is locked in an inactive state without activators and how autoinhibition is relieved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conformational changes in Arp2/3 complex induced by ATP, WASp-VCA, and actin filaments.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Sep 11;115(37):E8642-E8651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1717594115. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30150414 Free PMC article.
-
Role and structural mechanism of WASP-triggered conformational changes in branched actin filament nucleation by Arp2/3 complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jul 5;113(27):E3834-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1517798113. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27325766 Free PMC article.
-
NPF binding to Arp2 is allosterically linked to the release of ArpC5's N-terminal tail and conformational changes in Arp2/3 complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Feb 25;122(8):e2421557122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2421557122. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40042350
-
Signalling to actin assembly via the WASP (Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein)-family proteins and the Arp2/3 complex.Biochem J. 2004 May 15;380(Pt 1):1-17. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040176. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15040784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of nucleation promoting factors for directional actin filament elongation: allosteric regulation and multimerization on the membrane.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013 Apr;24(4):267-71. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2013.01.006. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23380397 Review.
Cited by
-
Conformational changes in Arp2/3 complex induced by ATP, WASp-VCA, and actin filaments.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Sep 11;115(37):E8642-E8651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1717594115. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30150414 Free PMC article.
-
Olaquindox disrupts tight junction integrity and cytoskeleton architecture in mouse Sertoli cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 16;8(51):88630-88644. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20289. eCollection 2017 Oct 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29179463 Free PMC article.
-
Synergy between Wsp1 and Dip1 may initiate assembly of endocytic actin networks.Elife. 2020 Nov 12;9:e60419. doi: 10.7554/eLife.60419. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33179595 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of actin filament branch formation by Arp2/3 complex revealed by a high-resolution cryo-EM structureof the branch junction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Dec 6;119(49):e2206722119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2206722119. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36442092 Free PMC article.
-
Partial loss of actin nucleator actin-related protein 2/3 activity triggers blebbing in primary T lymphocytes.Immunol Cell Biol. 2020 Feb;98(2):93-113. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12304. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Immunol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31698518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goley E. D. & Welch M. D. The ARP2/3 complex: an actin nucleator comes of age. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 713–726 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Rotty J. D., Wu C. & Bear J. E. New insights into the regulation and cellular functions of the ARP2/3 complex. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 7–12 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Achard V. et al.. A ‘primer'-based mechanism underlies branched actin filament network formation and motility. Curr. Biol. 20, 423–428 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Marchand J. B., Kaiser D. A., Pollard T. D. & Higgs H. N. Interaction of WASP/Scar proteins with actin and vertebrate Arp2/3 complex. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 76–82 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

