Vitamin D and Reproduction: From Gametes to Childhood
- PMID: 27417816
- PMCID: PMC4934634
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare3041097
Vitamin D and Reproduction: From Gametes to Childhood
Abstract
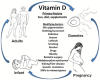
Vitamin D is well recognized for its essentiality in maintaining skeletal health. Recent research has suggested that vitamin D may exert a broad range of roles throughout the human life cycle starting from reproduction to adult chronic disease risk. Rates of vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy remain high worldwide. Vitamin D deficiency has been associated with an increased risk of fertility problems, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and allergic disease in the offspring. Vitamin D is found naturally in only a few foods thus supplementation can provide an accessible and effective way to raise vitamin D status when dietary intakes and sunlight exposure are low. However, the possibility of overconsumption and possible adverse effects is under debate. The effect of vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy and early life on maternal and infant outcomes will be of particular focus in this review.
Keywords: allergic disease; fertility; gestational diabetes; preeclampsia; pregnancy; toxicity; vitamin D; vitamin D supplementation.
Figures
References
-
- Holick M.F., Binkley N.C., Bischoff-Ferrari H.A., Gordon C.M., Hanley D.A., Heaney R.P., Murad M.H., Weaver C.M., Endocrine S. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011;96:1911–1930. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-0385. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources