Logical Reduction of Biological Networks to Their Most Determinative Components
- PMID: 27417985
- PMCID: PMC4993808
- DOI: 10.1007/s11538-016-0193-x
Logical Reduction of Biological Networks to Their Most Determinative Components
Abstract
Boolean networks have been widely used as models for gene regulatory networks, signal transduction networks, or neural networks, among many others. One of the main difficulties in analyzing the dynamics of a Boolean network and its sensitivity to perturbations or mutations is the fact that it grows exponentially with the number of nodes. Therefore, various approaches for simplifying the computations and reducing the network to a subset of relevant nodes have been proposed in the past few years. We consider a recently introduced method for reducing a Boolean network to its most determinative nodes that yield the highest information gain. The determinative power of a node is obtained by a summation of all mutual information quantities over all nodes having the chosen node as a common input, thus representing a measure of information gain obtained by the knowledge of the node under consideration. The determinative power of nodes has been considered in the literature under the assumption that the inputs are independent in which case one can use the Bahadur orthonormal basis. In this article, we relax that assumption and use a standard orthonormal basis instead. We use techniques of Hilbert space operators and harmonic analysis to generate formulas for the sensitivity to perturbations of nodes, quantified by the notions of influence, average sensitivity, and strength. Since we work on finite-dimensional spaces, our formulas and estimates can be and are formulated in plain matrix algebra terminology. We analyze the determinative power of nodes for a Boolean model of a signal transduction network of a generic fibroblast cell. We also show the similarities and differences induced by the alternative complete orthonormal basis used. Among the similarities, we mention the fact that the knowledge of the states of the most determinative nodes reduces the entropy or uncertainty of the overall network significantly. In a special case, we obtain a stronger result than in previous works, showing that a large information gain from a set of input nodes generates increased sensitivity to perturbations of those inputs.
Keywords: Biological information theory; Boolean networks; Linear operators; Mutual information; Network reduction; Numerical simulations; Sensitivity.
Figures

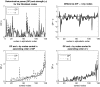
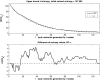
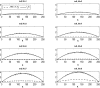
References
-
- Butte AJ, Kohane IS. Mutual information relevance networks: functional genomic clustering using pairwise entropy measurements. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2000;5:415–426. - PubMed
-
- Butte AJ, Kohane IS (2003) Relevance networks: a first step toward finding genetic regulatory networks within microarray data. In: Parmigiani G, Garett ES, Irizarry RA, Zeger SL (eds) The analysis of gene expression data. Part of the series statistics for biology and health. Springer, Berlin, pp 428–446
-
- Cover TM, Thomas JA (2006) Elements of information theory. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

