Primary hyperaldosteronism: a case of unilateral adrenal hyperplasia with contralateral incidentaloma
- PMID: 27417992
- PMCID: PMC4956976
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2016-216209
Primary hyperaldosteronism: a case of unilateral adrenal hyperplasia with contralateral incidentaloma
Abstract
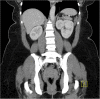
Primary hyperaldosteronism is one of the most common causes of secondary hypertension but clear differentiation between its various subtypes can be a clinical challenge. We report the case of a 37-year-old African-American woman with refractory hypertension who was admitted to our hospital for palpitations, shortness of breath and headache. Her laboratory results showed hypokalaemia and an elevated aldosterone/renin ratio. An abdominal CT scan showed a nodule in the left adrenal gland but adrenal venous sampling showed elevated aldosterone/renin ratio from the right adrenal vein. The patient began a new medical regimen but declined any surgical options. We recommend clinicians to maintain a high level of suspicion to consider the less common subtypes of primary hyperaldosteronism, especially given the fact that the management greatly varies.
2016 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Kucharz EJ. Michał Lityński—a forgotten author of the first description on primary hyperaldosteronism. Pol Arch Med Wewn 2007;117:57–8. - PubMed
-
- DeGroot L, Jameson J. Endocrinology. 4th edn Philadelphia: W.B. Sanders, 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
