Unequal representation of genetic variation across ancestry groups creates healthcare inequality in the application of precision medicine
- PMID: 27418169
- PMCID: PMC4944427
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-016-1016-y
Unequal representation of genetic variation across ancestry groups creates healthcare inequality in the application of precision medicine
Abstract
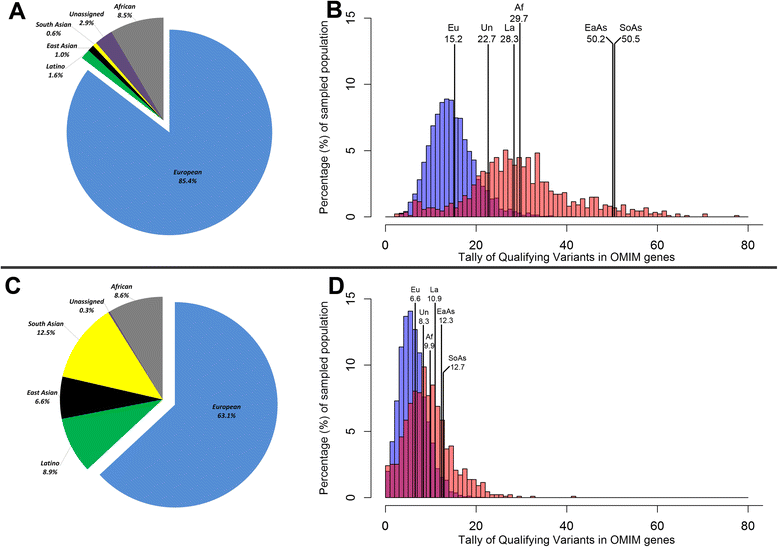
An important application of modern genomics is diagnosing genetic disorders. We use the largest publicly available exome sequence database to show that this key clinical service can currently be performed much more effectively in individuals of European genetic ancestry.
Keywords: Clinical diagnostics; Disease-associated genes; Genetic ancestry; Genetic variation; Geographic ancestry; Healthcare inequality; Next generation sequencing; Precision medicine; Rare variants; Sequence interpretation.
Figures
Comment in
-
Accurate and equitable medical genomic analysis requires an understanding of demography and its influence on sample size and ratio.Genome Biol. 2017 Feb 27;18(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1172-8. Genome Biol. 2017. PMID: 28241850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bustamante CD, Fledel-Alon A, Williamson S, Nielsen R, Hubisz MT, Glanowski S, Tanenbaum DM, White TJ, Sninsky JJ, Hernandez RD, et al. Natural selection on protein-coding genes in the human genome. Nature. 2005;437:1153–7. - PubMed
-
- Kimura M. The Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution. 1st ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1983. Cambridge Books Online. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511623486. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

