Development, roll-out and impact of Xpert MTB/RIF for tuberculosis: what lessons have we learnt and how can we do better?
- PMID: 27418550
- PMCID: PMC4967565
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.00543-2016
Development, roll-out and impact of Xpert MTB/RIF for tuberculosis: what lessons have we learnt and how can we do better?
Abstract
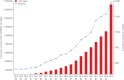
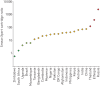
The global roll-out of Xpert MTB/RIF (Cepheid Inc., Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has changed the diagnostic landscape of tuberculosis (TB). More than 16 million tests have been performed in 122 countries since 2011, and detection of multidrug-resistant TB has increased three- to eight-fold compared to conventional testing. The roll-out has galvanised stakeholders, from donors to civil society, and paved the way for universal drug susceptibility testing. It has attracted new product developers to TB, resulting in a robust molecular diagnostics pipeline. However, the roll-out has also highlighted gaps that have constrained scale-up and limited impact on patient outcomes. The roll-out has been hampered by high costs for under-funded programmes, unavailability of a complete solution package (notably comprehensive training, quality assurance, implementation plans, inadequate service and maintenance support) and lack of impact assessment. Insufficient focus has been afforded to effective linkage to care of diagnosed patients, and clinical impact has been blunted by weak health systems. In many countries the private sector plays a dominant role in TB control, yet this sector has limited access to subsidised pricing. In light of these lessons, we advocate for a comprehensive diagnostics implementation approach, including increased engagement of in-country stakeholders for product launch and roll-out, broader systems strengthening in preparation for new technologies, as well as quality impact data from programmatic settings.
Copyright ©ERS 2016.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Disclosures can be found alongside the online version of this article at
Figures

Comment in
-
Tuberculosis prevention must integrate technological and basic care innovation.Eur Respir J. 2016 Nov;48(5):1529-1531. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01449-2016. Eur Respir J. 2016. PMID: 27799402 Free PMC article.
-
Tuberculosis prevention must integrate technological and basic care innovation.Eur Respir J. 2016 Nov;48(5):1531-1532. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01601-2016. Eur Respir J. 2016. PMID: 27799403 No abstract available.
References
-
- Weyer K, Mirzayev F, Migliori GB, et al. . Rapid molecular TB diagnosis: evidence, policy making and global implementation of Xpert MTB/RIF. Eur Respir J 2013; 42: 252–271. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Policy statement: automated real-time nucleic acid amplification technology for rapid and simultaneous detection of tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance: Xpert MTB/RIF. Policy statement Geneva, World Health Organization, 2011.
-
- Ramsay ARC, Steingart KR, Cunningham J, et al. . Translating tuberculosis research into global policies: the example of an international collaboration on diagnostics. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2011; 15: 1283–1293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
