Zika Virus Infection Associated With Severe Thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 27418575
- PMCID: PMC5176332
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciw476
Zika Virus Infection Associated With Severe Thrombocytopenia
Abstract
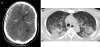
We report two patients that developed severe thrombocytopenia after Zika virus (ZIKV) infection. The first patient had 1000 platelets/μL and died after multiple hemorrhages. The second patient had 2000 platelets/μL, had melena and ecchymoses, and recovered after receiving intravenous immunoglobulin. ZIKV may be associated with immune-mediated severe thrombocytopenia.
Keywords: Puerto Rico; Zika virus; fatal; thrombocytopenia.
Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America 2016. This work is written by (a) US Government employee(s) and is in the public domain in the US.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Simmons CP, Farrar JJ, Nguyen VV, Wills B. Dengue. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1423–32. - PubMed
-
- Ruzek D, Yakimenko VV, Karan LS, Tkachev SE. Omsk haemorrhagic fever. Lancet. 2010;376:2104–13. - PubMed
-
- Monath TP, Vasconcelos PF. Yellow fever. J Clin Virol. 2015;64:160–73. - PubMed
-
- Petersen LR, Jamieson DJ, Powers AM, Honein MA. Zika virus. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1552–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

