Clinical characteristics and long term post-operative outcome of cardiac myxoma
- PMID: 27418902
- PMCID: PMC4943072
Clinical characteristics and long term post-operative outcome of cardiac myxoma
Abstract
Background and aim: Myxoma is the most common type of primary cardiac neoplasm, but the clinical characteristics and long term outcome are less known in the elderly in China.
Methods: We analyzed medical records of 112 consecutive patients who underwent operative resection of cardiac myxoma between December 1988 and December 2010 in our hospital. Their data were retrospectively analyzed and the difference between two age groups (< 60 years, n = 87 and ≥ 60 years, n = 25) was compared.
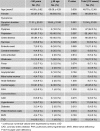
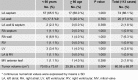
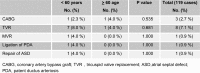
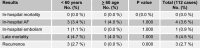
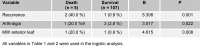
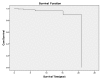
Results: The mean age of 112 patients was 48.8 ± 12.5 (range 13 ~ 75) years, and 66 patients (58.9 %) were female. The interval from onset of symptoms to diagnosis was 12 months and the most common presenting symptoms were chest distress (66 patients 58.9 %), followed by palpitations (55 patients, 49.1 %) and dyspnea (47 patients, 42.0 %). Mitral valve diastolic murmur was heard in 67 (59.1 %) patients. The tumor was located in the left atrium in 96 (85.8 %) patients. There were no in-hospital death. During follow-up ranged between one and twenty-one (7.3 ± 5.3) years, there was no malignancy. Myxoma recurred in 3 (2.7 %) patients and deaths occurred in 5 (4.5 %) patients. The 5 and 15 years survival was 97.8 % and 89.5 %, respectively. To compare with the younger patients, the elderly have higher ratios of concomitant hypertension, fewer complaints of dyspnea and chest distress (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The elderly have lower complaints of dyspnea and chest distress, surgical treatment is associated with low long-term mortality and recurrence rate even in the elder patients.
Keywords: cardiac myxoma; clinical characteristics; outcome; the elderly.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Cardiac myxoma: clinical characterization, diagnostic methods and late surgical results].Rev Med Chil. 2008 Mar;136(3):287-95. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Rev Med Chil. 2008. PMID: 18575653 Spanish.
-
Cardiac myxoma: sixteen-year experience in Central Chest Institute of Thailand.J Med Assoc Thai. 2012 Dec;95(12):1509-16. J Med Assoc Thai. 2012. PMID: 23390780
-
Cardiac myxoma: clinical characteristics, surgical intervention, intra-operative challenges and outcome.Perfusion. 2017 Nov;32(8):686-690. doi: 10.1177/0267659117722596. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Perfusion. 2017. PMID: 28762298
-
Clinical presentation of left atrial cardiac myxoma. A series of 112 consecutive cases.Medicine (Baltimore). 2001 May;80(3):159-72. doi: 10.1097/00005792-200105000-00002. Medicine (Baltimore). 2001. PMID: 11388092 Review.
-
Mitral valve recurrence of a left atrial myxoma.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002 Mar;21(3):568-73. doi: 10.1016/s1010-7940(02)00023-4. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002. PMID: 11888789 Review.
Cited by
-
Atrial myxoma presenting as infective endocarditis.BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Mar 9;2018:bcr2017223656. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-223656. BMJ Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29525758 Free PMC article.
-
Detection, Prevention, and Treatment of Asymptomatic Myxoma in a Young Adult Patient: A Case Report.Cureus. 2025 Apr 3;17(4):e81649. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81649. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40322406 Free PMC article.
-
Tumoration in Anterior Leaflet of the Mitral Valve.Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2021 Feb 1;36(1):116-119. doi: 10.21470/1678-9741-2020-0557. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 33594865 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Attum AA, Johnson GS, Masri Z, Girardet R, Lansing AM. Malignant clinical behaveior of cardiac myxomas and "myxoid imitators". Ann Thorac Surg. 1987;44:217–222. - PubMed
-
- Becker RP, Ramírez MA, Zalaquett SR, Moran VS, Irarrázaval LI MJ, Arretz VC, et al. Cardiac myxoma: clinical characterization, diagnostic methods and late surgical results. Rev Med Chil. 2008;136:287–295. - PubMed
-
- Bhan A, Mehrotra R, Choudhary SK, Sharma R, Prabhakar D, Airan B, et al. Surgical experience with intracardiac myxomas: long-term follow-up. Ann Thorac Surg. 1998;66:810–813. - PubMed
-
- Centofanti P, Di Rosa E, Deorsola L, Dato GM, Patanè F, La Torre M, et al. Primary cardiac tumors: early and late results of surgical treatment in 91 patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 1999;68:1236–1241. - PubMed
-
- Cleveland DC, Westaby S, Karp RB. Treatment of intra atrial cardiac tumors. JAMA. 1983;249:2799–2802. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
