Hypocholesterolemic effect of an aqueous extract of the leaves of Sansevieria senegambica Baker on plasma lipid profile and atherogenic indices of rats fed egg yolk supplemented diet
- PMID: 27418909
- PMCID: PMC4941801
Hypocholesterolemic effect of an aqueous extract of the leaves of Sansevieria senegambica Baker on plasma lipid profile and atherogenic indices of rats fed egg yolk supplemented diet
Abstract
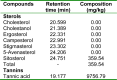
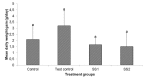
The effects of an aqueous extract of the leaves of Sansevieria senegambica on daily weight gain, lipid profile and atherogenic indices of rats fed egg yolk supplemented diet was studied. The control group was given normal feed while the other three groups received 50 g egg yolk/kg feed. The extract was orally administered daily at 150 and 200 mg/kg body weight; while the test control and control groups received appropriate volumes of water by the same route. On gas chromatographic analysis of the aqueous crude extract, the phytosterol and tannins fractions contained 100 % of β-sitosterol and tannic acid respectively. The mean daily weight gain of the test control group was higher though not significantly, than those of the other groups. The plasma total cholesterol levels, cardiac risk ratio and atherogenic coefficient of the test control group was significantly higher (P<0.05) than those of the test groups, but not significantly higher than that of the control group. The plasma low density lipoprotein and non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels of the test control group was significantly higher (P<0.05) than those of the control and test groups. The plasma high density lipoprotein cholesterol of the test control group was significantly lower (P<0.05) than that of the control group, but not significantly lower than those of the test groups. There were no significant differences in the plasma triglyceride and very low density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, and the atherogenic index of plasma of all the groups. These results indicate a dose-dependent hypocholesterolemic effect of the extract, thus suggesting a likely protective role of the extract against the development of cardiovascular diseases. It also revealed the presence of pharmacologically active agents in the leaves.
Keywords: Sansevieria senegambica; atherogenic indices; beta-sitosterol; lipid profile; tannic acid.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Moderation of hematological and plasma biochemical indices of sub-chronic salt-loaded rats by aqueous extract of the sclerotia of Pleurotus tuberregium (Fr) Sing's: implications for the reduction of cardiovascular risk.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Nov 25;150(2):466-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.09.002. Epub 2013 Sep 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24055467
-
Effect of aqueous extract of the leaves of Acalypha wilkesiana 'Godseffiana' Muell Arg (Euphorbiaceae) on the hematology, plasma biochemistry and ocular indices of oxidative stress in alloxan induced diabetic rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Oct 11;137(3):1415-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.015. Epub 2011 Aug 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21864665
-
Positive moderation of the hematology, plasma biochemistry and ocular indices of oxidative stress in alloxan-induced diabetic rats, by an aqueous extract of the leaves of Sansevieria liberica Gerome and Labroy.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2013 Jan;6(1):27-36. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(12)60196-5. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2013. PMID: 23317882
-
Fatty acid and cholesterol profiles and hypocholesterolemic, atherogenic, and thrombogenic indices of table eggs in the retail market.Lipids Health Dis. 2015 Oct 27;14:136. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0133-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2015. PMID: 26507616 Free PMC article.
-
Hypocholesterolemic effect of karaya saponin in Japanese laying quails (Coturnix coturnix japonica).J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2011 Dec;95(6):693-700. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0396.2010.01098.x. Epub 2010 Nov 28. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2011. PMID: 21114549 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Analysis of Oat (Avena sativa L.) and Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Saponins in Plant-Based Food Products by Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry.Foods. 2023 Feb 26;12(5):991. doi: 10.3390/foods12050991. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36900507 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative Effect of Hydroethanolic Leaf Extract of Byrsocarpus coccineus in Alcohol- and Sucrose-Induced Hypertension in Rats.J Tradit Complement Med. 2014 Jul;4(3):177-88. doi: 10.4103/2225-4110.129562. J Tradit Complement Med. 2014. PMID: 25161923 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive Potential of the Aqueous Extract of the Mixture of Bidens pilosa (Asteraceae) and Cymbopogon citratus (Poaceae) Aerial Parts on Hypertension Induced by a Chronic Salt and Alcohol Consumption on the Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Mar 9;2022:1980622. doi: 10.1155/2022/1980622. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35310038 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological study on the influence of some plant oils in rats exposed to a sublethal concentration of diazinon.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018 May;25(4):786-796. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.11.002. Epub 2016 Nov 10. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29740245 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agbafor KN, Akubugwo EI. Hypocholesterolaemic effect of ethanolic extract of fresh leaves of Cymbopogon citrates (lemongrass) Afr J Biotech. 2007;6:596–598.
-
- AOAC, Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Cholesterol in foods. Direct saponification-gas chromatographic method. AOAC Official Method 994.10. Gaithersberg (USA): AOAC International; 2000.
-
- AOAC, Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Oil in seeds. Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) method. AOAC Official Method 999.02. Gaithersberg (USA): AOAC International; 2002.
-
- Assmann G, Gotto AM., Jr HDL cholesterol and protective factors in atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2004;109(Suppl III):III–8–III. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
