A novel hybrid method of beta-turn identification in protein using binary logistic regression and neural network
- PMID: 27418910
- PMCID: PMC4941805
A novel hybrid method of beta-turn identification in protein using binary logistic regression and neural network
Abstract
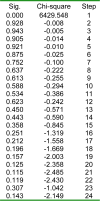
From both the structural and functional points of view, β-turns play important biological roles in proteins. In the present study, a novel two-stage hybrid procedure has been developed to identify β-turns in proteins. Binary logistic regression was initially used for the first time to select significant sequence parameters in identification of β-turns due to a re-substitution test procedure. Sequence parameters were consisted of 80 amino acid positional occurrences and 20 amino acid percentages in sequence. Among these parameters, the most significant ones which were selected by binary logistic regression model, were percentages of Gly, Ser and the occurrence of Asn in position i+2, respectively, in sequence. These significant parameters have the highest effect on the constitution of a β-turn sequence. A neural network model was then constructed and fed by the parameters selected by binary logistic regression to build a hybrid predictor. The networks have been trained and tested on a non-homologous dataset of 565 protein chains. With applying a nine fold cross-validation test on the dataset, the network reached an overall accuracy (Qtotal) of 74, which is comparable with results of the other β-turn prediction methods. In conclusion, this study proves that the parameter selection ability of binary logistic regression together with the prediction capability of neural networks lead to the development of more precise models for identifying β-turns in proteins.
Keywords: beta-turns; binary logistic regression; neural networks; secondary structure prediction; sequence parameters.
Figures



Similar articles
-
RETRACTED: Analysis and prediction of β-turn types using multinomial logistic regression and artificial neural network.Bioinformatics. 2019 Jun 1;35(12):e8-e15. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm094. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 17379690
-
Analysis and identification of beta-turn types using multinomial logistic regression and artificial neural network.Bioinformatics. 2007 Dec 1;23(23):3125-30. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm324. Epub 2007 Jun 28. Bioinformatics. 2007. Retraction in: Bioinformatics. 2019 Jun 1;35(12):e8-e15. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm094. PMID: 17599929 Retracted.
-
A neural network method for prediction of beta-turn types in proteins using evolutionary information.Bioinformatics. 2004 Nov 1;20(16):2751-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth322. Epub 2004 May 14. Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15145798
-
Prediction of tight turns and their types in proteins.Anal Biochem. 2000 Nov 1;286(1):1-16. doi: 10.1006/abio.2000.4757. Anal Biochem. 2000. PMID: 11038267 Review.
-
[A turning point in the knowledge of the structure-function-activity relations of elastin].J Soc Biol. 2001;195(2):181-93. J Soc Biol. 2001. PMID: 11727705 Review. French.
References
-
- Asgary MP, Jahandideh S, Abdolmaleki P, Kazemnejad A. Analysis and identification of β-turn types using multinomial logistic regression and artificial neural network. Biinformatics. 2007;23:3125–3130. - PubMed
-
- Cai YD, Liu XJ, Li YX, Xu XB, Chou KC. Prediction of β-turns with learning machines. Peptides. 2003;24:665–669. - PubMed
-
- Chou KC. Prediction of tight turns and their types in proteins. Anal Biochem. 2000;286:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Chou PY, Fasman GD. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, β-sheet and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry. 1974;13:211–222. - PubMed
-
- Fuchs PFJ, Alix AJP. High accuracy prediction of β-turns and their types using propensities and multiple alignments. Proteins. 2005;59:828–839. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
