Characterization of AmtA, an amidinotransferase involved in the biosynthesis of phaseolotoxins
- PMID: 27419063
- PMCID: PMC4887976
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.12071
Characterization of AmtA, an amidinotransferase involved in the biosynthesis of phaseolotoxins
Abstract
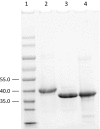
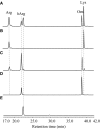
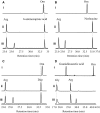
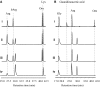
Phaseolotoxins (PHTs), which are produced by Pseudomonas, belong to a family of phosphoramidate natural products. Two nonproteinogenic amino acid precursors, N(δ)(N'-sulfo-diaminophosphinyl)-ornithine (PSOrn) and homoarginine (hArg), are involved in biosynthesis of PHTs. Amidinotransferase AmtA catalyses the formation of hArg, with arginine and lysine as substrates. AmtA was overexpressed and purified in an Escherichia coli system. An in vitro enzyme assay showed that it has stricter substrate specificity than certain other amidinotransferases. Site-directed mutagenesis experiments showed that the mutation AmtA Met243His244 is an alternative while Met246 is essential for the transamidination activity.
Keywords: amidinotransferase; biosynthesis; homoarginine; phaseolotoxin.
Figures



References
-
- Gross H and Loper JE (2009) Genomics of secondary metabolite production by Pseudomonas spp. Nat Prod Rep 26, 1408–1446. - PubMed
-
- Renzi M, Copini P, Taddei AR, Rossetti A, Gallipoli L, Mazzaglia A and Balestra GM (2012) Bacterial canker on kiwifruit in Italy: anatomical changes in the wood and in the primary infection sites. Phytopathology 102, 827–840. - PubMed
-
- Langley DB, Templeton MD, Fields BA, Mitchell RE and Collyer CA (2000) Mechanism of inactivation of ornithine transcarbamoylase by Nδ‐(N′‐Sulfodiaminophosphinyl)‐L‐ornithine, a true transition state analogue? Crystal structure and implications for catalytic mechanism. J Biol Chem 275, 20012–20019. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

