The eye of the Barbary sheep or aoudad (Ammotragus lervia): reference values for selected ophthalmic diagnostic tests, morphologic and biometric observations
- PMID: 27419103
- PMCID: PMC4935764
- DOI: 10.4314/ovj.v6i2.6
The eye of the Barbary sheep or aoudad (Ammotragus lervia): reference values for selected ophthalmic diagnostic tests, morphologic and biometric observations
Abstract
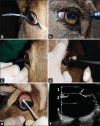
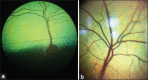
The purpose of this study was to describe the normal ocular anatomy and establish reference values for ophthalmic tests in the Barbary sheep or aoudad (Ammotragus lervia). Aoudad eyes are large and laterally positioned in the head with several specialized anatomic features attributed to evolutionary adaptations for grazing. Normal values for commonly used ophthalmic tests were established, Schirmer tear test (STT) - 27.22 ± 3.6 mm/min; Predominant ocular surface bacterial microbiota - Staphylococcus sp.; Corneal esthesiometry- 1.3 ± 0.4 cm; Intraocular pressure by rebound tonometry- 19.47 ± 3.9 mmHg; Corneal thickness- 630.07 ± 20.67 µm, B-mode ultrasonography of the globe-axial eye globe length 29.94 ± 0.96 mm, anterior chamber depth 5.03 ± 0.17 mm, lens thickness 9.4 ± 0.33 mm, vitreous chamber depth 14.1 ± 0.53 mm; Corneal diameter-horizontal corneal diameter 25.05 ± 2.18 mm, vertical corneal diameter 17.95 ± 1.68 mm; Horizontal palpebral fissure length- 34.8 ± 3.12 mm. Knowledge of these normal anatomic variations, biometric findings and normal parameters for ocular diagnostic tests may assist veterinary ophthalmologists in the diagnosis of ocular diseases in this and other similar species.
Keywords: Barbary sheep; Biometry; Ocular parameters; Wild caprid.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The eye of the red-eared slider turtle: morphologic observations and reference values for selected ophthalmic diagnostic tests.Vet Ophthalmol. 2015 Jan;18 Suppl 1:61-70. doi: 10.1111/vop.12213. Epub 2014 Sep 10. Vet Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25209440
-
The crested caracara (Caracara plancus) eye: Morphologic observations and results of selected diagnostic tests.Vet Ophthalmol. 2021 Sep;24(5):533-542. doi: 10.1111/vop.12939. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Vet Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34554632
-
Ophthalmic Diagnostic Tests and Ocular Findings in a Flock of Captive American Flamingos ( Phoenicopterus ruber ruber).J Avian Med Surg. 2015 Jun;29(2):95-105. doi: 10.1647/2014-021. J Avian Med Surg. 2015. PMID: 26115208
-
THE EYE OF THE AZARA'S AGOUTI ( DASYPROCTA AZARAE): MORPHOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS AND SELECTED OPHTHALMIC DIAGNOSTIC TESTS.J Zoo Wildl Med. 2017 Dec;48(4):1108-1119. doi: 10.1638/1042-7260-48.4.1108. J Zoo Wildl Med. 2017. PMID: 29297794
-
The capybara eye: clinical tests, anatomic and biometric features.Vet Ophthalmol. 2008 Nov-Dec;11(6):386-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-5224.2008.00663.x. Vet Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 19046280
Cited by
-
Measurement of tear production and intraocular pressure in conscious captive European fallow deer (DAMA dama).Vet Med Sci. 2018 Jun 1;4(3):227-36. doi: 10.1002/vms3.105. Online ahead of print. Vet Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29855155 Free PMC article.
-
Normal Range for the Schirmer Tear Test and Intraocular Pressure in Healthy Latvian Darkhead Lambs and Ewes.Vet Sci. 2023 Jun 8;10(6):392. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10060392. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37368778 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Genome Resequencing Reveals Artificial and Natural Selection for Visual Deterioration, Plateau Adaptability and High Prolificacy in Chinese Domestic Sheep.Front Genet. 2019 Apr 2;10:300. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00300. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31001329 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound, Dacryocystorhinography and Morphological Examination of Normal Eye and Lacrimal Apparatus of the Donkey (Equus asinus).Animals (Basel). 2022 Jan 6;12(2):132. doi: 10.3390/ani12020132. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35049756 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abáigar T, Domené M.A, Cassinello J. Characterization of the estrous cycle and reproductive traits of the aoudad (Ammotragus lervia) in captivity. Theriogenology. 2012;77:1759–1766. - PubMed
-
- Alados C, Shackleton D.M. Regional Summary. In: Shackleton D.M, editor. Wild Sheep and Goats and Their Relatives, Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan for Caprinae. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN; 1997. pp. 47–48.
-
- Alario A.F, Pirie C.G. Central corneal thickness measurements in normal dogs, a comparison between ultrasound pachymetry and optical coherence tomography. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2014;17:207–211. - PubMed
-
- Andrew S.E, Nguyen A, Jones G.L, Brooks D.E. Seasonal effects on the aerobic bacterial and fungal conjunctival flora of normal thoroughbred brood mares in Florida. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2003;6:45–50. - PubMed
-
- Assadnassab G, Fartashvan M. Ultrasonographic evaluation of buffalo eyes. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2013;37:395–39.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
