Trends in Outcomes, Financial Burden, and Mortality for Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) in the United States from 2002 to 2010
- PMID: 27419254
- PMCID: PMC5626565
- DOI: 10.1080/15412555.2016.1199669
Trends in Outcomes, Financial Burden, and Mortality for Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) in the United States from 2002 to 2010
Abstract
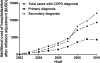
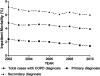
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is the cause of substantial economic and social burden. We evaluated the temporal trends of hospitalizations from acute exacerbation of COPD and determined its outcome and financial impact using the National (Nationwide) Inpatient Sample (NIS) databases (2002-2010). Individuals aged ≥ 18 years were included. Subjects who were hospitalized with primary diagnosis of COPD exacerbation and those who were admitted for other causes but had underlying acute exacerbation of COPD (secondary diagnosis) were captured by International Classification of Diseases-Ninth Revision (ICD-9) codes. The hospital outcomes and length of stay were determined. Multivariate logistic regression was used to identify the independent predictors of inpatient mortality. Overall acute exacerbation of COPD-related hospitalizations accounted for nearly 3.31% of all hospitalizations in the year 2002. This did not change significantly to year 2010 (3.43%, p = 0.608). However, there was an increase in hospitalization with secondary diagnosis of COPD. Elderly white patients accounted for most of the hospitalizations. Medicare was the primary payer source for most of the hospitalizations (73-75%). There was a significant decrease in inpatient mortality from 4.8% in 2002 to 3.9% in 2010 (slope -0.096, p < 0.001). Similarly, there was a significant decrease in average length of stay from 6.4 days in 2002 to 6.0 days in 2010 (slope -0.042, p < 0.001). Despite this, the hospitalization cost was increased substantially from $22,187 in 2002 to $38,455 in 2010. However, financial burden has increased over the years.
Keywords: COPD; NIS data; hospitalization costs; mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflicts with the contents and the results of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Calverley P, Pauwels R, Vestbo J, Jones P, Pride N, Gulsvik A, et al. Combined salmeterol and fluticasone in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361(9356):449–56. - PubMed
-
- Calverley PM, Walker P. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 2003;362(9389):1053–61. - PubMed
-
- Calverley PM, Anderson JA, Celli B, Ferguson GT, Jenkins C, Jones PW, et al. Salmeterol and fluticasone propionate and survival in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(8):775–89. - PubMed
-
- Vestbo J, Hurd SS, Agusti AG, Jones PW, Vogelmeier C, Anzueto A, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187(4):347–65. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
