Biological markers for anxiety disorders, OCD and PTSD: A consensus statement. Part II: Neurochemistry, neurophysiology and neurocognition
- PMID: 27419272
- PMCID: PMC5341771
- DOI: 10.1080/15622975.2016.1190867
Biological markers for anxiety disorders, OCD and PTSD: A consensus statement. Part II: Neurochemistry, neurophysiology and neurocognition
Abstract
Objective: Biomarkers are defined as anatomical, biochemical or physiological traits that are specific to certain disorders or syndromes. The objective of this paper is to summarise the current knowledge of biomarkers for anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Methods: Findings in biomarker research were reviewed by a task force of international experts in the field, consisting of members of the World Federation of Societies for Biological Psychiatry Task Force on Biological Markers and of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Anxiety Disorders Research Network.
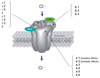
Results: The present article (Part II) summarises findings on potential biomarkers in neurochemistry (neurotransmitters such as serotonin, norepinephrine, dopamine or GABA, neuropeptides such as cholecystokinin, neurokinins, atrial natriuretic peptide, or oxytocin, the HPA axis, neurotrophic factors such as NGF and BDNF, immunology and CO2 hypersensitivity), neurophysiology (EEG, heart rate variability) and neurocognition. The accompanying paper (Part I) focuses on neuroimaging and genetics.
Conclusions: Although at present, none of the putative biomarkers is sufficient and specific as a diagnostic tool, an abundance of high quality research has accumulated that should improve our understanding of the neurobiological causes of anxiety disorders, OCD and PTSD.
Keywords: Anxiety disorders; genetic; neurobiology; neurochemistry; neuroimaging; review.
Conflict of interest statement
All other authors reported no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Abelli M, Chelli B, Costa B, Lari L, Cardini A, Gesi C, Muti M, Lucacchini A, Martini C, Cassano GB, et al. Reductions in platelet 18-kDa translocator protein density are associated with adult separation anxiety in patients with bipolar disorder. Neuropsychobiology. 2010;62:98–103. - PubMed
-
- Abelson JL, Curtis GC. Cardiac and neuroendocrine responses to exposure therapy in height phobics: desynchrony within the ‘physiological response system’. Behav Res Ther. 1989;27:561–567. - PubMed
-
- Abelson JL, Curtis GC, Cameron OG. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity in panic disorder: effects of alprazolam on 24 h secretion of adrenocorticotropin and cortisol. J Psychiatr Res. 1996;30:79–93. - PubMed
-
- Abelson JL, Khan S, Liberzon I, Young EA. HPA axis activity in patients with panic disorder: review and synthesis of four studies. Depress Anxiety. 2007;24:66–76. - PubMed
-
- Aboitiz F. Dynamics of neuromodulators–I. The role of dopaminergic signaling in goal-directed behavior. In: Aboitiz F, Cosmelli D, editors. From attention to goal-directed behavior. Heidelberg, Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 2009. pp. 187–204.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
