Postnatal growth of the human optic nerve
- PMID: 27419835
- PMCID: PMC5129860
- DOI: 10.1038/eye.2016.141
Postnatal growth of the human optic nerve
Abstract
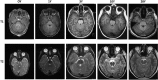
PurposeAlthough the length of the average human adult optic nerve (ON) is known, the average length of the normal full-term, newborn ON has never been adequately evaluated, nor has the in vivo growth rate of the human ON been determined. We wanted to identify both the average length of the newborn human ON and its rate of anteroposterior growth.Patients and methodsUsing MRIs from a newly generated set of normal newborn infants rescanned at 1 year, and from different aged groups, we calculated average newborn ON length and growth rate.ResultsThe newborn human ON is 25.3±0.3 mm in length from globe to chiasm, and grows by 80% in length after birth, with maximum speed of elongation occurring in the first 3 years of life, attaining full length by 15 years of age.ConclusionThe human ON grows dramatically in the first 3 years of life, and continues to grow for the first two decades. These data are relevant for pediatric treatments that may impede or alter orbital growth in infants, and maximal susceptibility to oncological procedures in early childhood.
Figures

References
-
- Scammon RE, Armstrong EL. On the growth of the human eyeball and optic nerve. J Comp Neurol 1925; 38: 165–219.
-
- Miller NR. Embryology of the afferent visual system. In: Walsh and Hoyt's Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology, Vol 1, 4th edn. Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1982, pp 3–10..
-
- Goldberg JL. How does an axon grow? Genes Dev 2003; 17: 941–958. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

