Involvement of Acylated Homoserine Lactones (AHLs) of Aeromonas sobria in Spoilage of Refrigerated Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.)
- PMID: 27420072
- PMCID: PMC4970129
- DOI: 10.3390/s16071083
Involvement of Acylated Homoserine Lactones (AHLs) of Aeromonas sobria in Spoilage of Refrigerated Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.)
Abstract
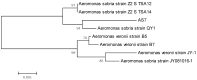
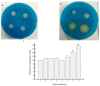
One quorum sensing strain was isolated from spoiled turbot. The species was determined by 16S rRNA gene analysis and classical tests, named Aeromonas sobria AS7. Quorum-sensing (QS) signals (N-acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs)) were detected by report strains and their structures were further determined by GC-MS. The activity changes of AHLs on strain growth stage as well as the influence of different culture conditions on secretion activity of AHLs were studied by the punch method. The result indicated that strain AS7 could induce report strains to produce typical phenotypic response. N-butanoyl-dl-homoserine lactone (C₄-HSL), N-hexanoyl-dl-homoserine lactone (C₆-HSL), N-octanoyl-dl-homoserine lactone (C₈-HSL), N-decanoyl-dl-homoserine lactone (C10-HSL), N-dodecanoyl-dl-homoserine lactone (C12-HSL) could be detected. The activities of AHLs were density-dependent and the max secretion level was at pH 8, sucrose culture, 1% NaCl and 32 h, respectively. The production of siderophore in strain AS7 was regulated by exogenous C₈-HSL, rather than C₆-HSL. Exogenous C₄-HSL and C₈-HSL accelerated the growth rate and population density of AS7 in turbot samples under refrigerated storage. However, according to the total viable counts and total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) values of the fish samples, exogenous C₆-HSL did not cause spoilage of the turbot fillets. In conclusion, our results suggested that QS was involved in the spoilage of refrigerated turbot.
Keywords: Aeromonas sobria; quorum sensing; siderophore; spoilage; turbot.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Characterization of N-acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs) producing bacteria isolated from vacuum-packaged refrigerated turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) and possible influence of exogenous AHLs on bacterial phenotype.J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2016;62(2):60-7. doi: 10.2323/jgam.62.60. J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27118073
-
Proteomic assessment of the role of N-acyl homoserine lactone in Shewanella putrefaciens spoilage.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2017 Nov;65(5):388-394. doi: 10.1111/lam.12795. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28833381
-
Quorum sensing asaI mutants affect spoilage phenotypes, motility, and biofilm formation in a marine fish isolate of Aeromonas salmonicida.Food Microbiol. 2018 Dec;76:40-51. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2018.04.009. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Food Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30166167
-
Production of N-acyl homoserine lactones by Chromobacterium haemolyticum KM2 isolated from the river water in Malaysia.Arch Microbiol. 2018 Sep;200(7):1135-1142. doi: 10.1007/s00203-018-1526-y. Epub 2018 May 23. Arch Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29796703
-
Recent Advances in the Mechanisms and Regulation of QS in Dairy Spoilage by Pseudomonas spp.Foods. 2021 Dec 13;10(12):3088. doi: 10.3390/foods10123088. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34945641 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spoilage of refrigerated Litopenaeus vannamei: eavesdropping on Acinetobacter acyl-homoserine lactones promotes the spoilage potential of Shewanella baltica.J Food Sci Technol. 2018 May;55(5):1903-1912. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3108-z. Epub 2018 Mar 15. J Food Sci Technol. 2018. PMID: 29666543 Free PMC article.
-
The Social Life of Aeromonas through Biofilm and Quorum Sensing Systems.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jan 20;8:37. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00037. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28163702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of Exogenous N-Acyl-Homoserine Lactones in Spoilage Potential of Pseudomonas fluorescens Isolated From Refrigerated Turbot.Front Microbiol. 2019 Nov 29;10:2716. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02716. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31849873 Free PMC article.
-
Growth-Stimulatory Effect of Quorum Sensing Signal Molecule N-Acyl-Homoserine Lactone-Producing Multi-Trait Aeromonas spp. on Wheat Genotypes Under Salt Stress.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 29;11:553621. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.553621. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33117303 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum-Sensing Inhibition by Gram-Positive Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2022 Feb 3;10(2):350. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020350. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35208805 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang H.H., Ye K.P., Zhang Q.Q., Dong Y., Xu X.L., Zhou G.H. Biofilm formation of meat-borne Salmonella enterica and inhibition by the cell-free supernatant from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Food Control. 2013;32:650–658. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.01.047. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

