HBx mutations promote hepatoma cell migration through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- PMID: 27420729
- PMCID: PMC5084678
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13014
HBx mutations promote hepatoma cell migration through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Abstract
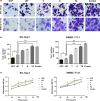
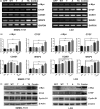
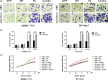
HBx mutations (T1753V, A1762T, G1764A, and T1768A) are frequently observed in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Aberrant activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is involved in the development of HCC. However, activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by HBx mutants has not been studied in hepatoma cells or HBV-associated HCC samples. In this study, we examined the effects of HBx mutants on the migration and proliferation of HCC cells and evaluated the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in HBx-transfected HCC cells and HBV-related HCC tissues. We found that HBx mutants (T, A, TA, and Combo) promoted the migration and proliferation of hepatoma cells. The HBx Combo mutant potentiated TOP-luc activity and increased nuclear translocation of β-catenin. Moreover, the HBx Combo mutant increased and stabilized β-catenin levels through inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β, resulting in upregulation of downstream target genes such as c-Myc, CTGF, and WISP2. Enhanced activation of Wnt/β-catenin was found in HCC tissues with HBx TA and Combo mutations. Knockdown of β-catenin effectively abrogated cell migration and proliferation stimulated by the HBx TA and Combo mutants. Our results indicate that HBx mutants, especially the Combo mutant, allow constitutive activation of the Wnt signaling pathway and may play a pivotal role in HBV-associated hepatocarcinogenesis.
Keywords: GSK-3β; HBx mutants; Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway; hepatitis B virus; hepatocellular carcinoma.
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epigenetic silencing of SFRP1 and SFRP5 by hepatitis B virus X protein enhances hepatoma cell tumorigenicity through Wnt signaling pathway.Int J Cancer. 2014 Aug 1;135(3):635-46. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28697. Epub 2014 Jan 13. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24374650
-
Hepatitis B virus core promoter mutations contribute to hepatocarcinogenesis by deregulating SKP2 and its target, p21.Gastroenterology. 2011 Oct;141(4):1412-21, 1421.e1-5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.06.048. Epub 2011 Jun 24. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21704589 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of aberrant Wnt signaling in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 May 28;21(20):6317-28. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6317. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26034368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell cycle-related kinase mediates viral-host signalling to promote hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocarcinogenesis.Gut. 2014 Nov;63(11):1793-804. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305584. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Gut. 2014. PMID: 24440987
-
Interplay of Wnt β-catenin pathway and miRNAs in HBV pathogenesis leading to HCC.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug;43(4):373-386. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2018.09.012. Epub 2018 Oct 28. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30377095 Review.
Cited by
-
CRISPR/Cas9 as a New Antiviral Strategy for Treating Hepatitis Viral Infections.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 26;25(1):334. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010334. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanisms of progression and immunotherapy.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jul 7;25(25):3151-3167. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i25.3151. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31333308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of WISP proteins in tumorigenesis and cancer therapy.J Transl Med. 2019 Jan 16;17(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1769-7. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30651114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current updates on the molecular and genetic signals as diagnostic and therapeutic targets for hepatitis B virus-associated hepatic malignancy.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 8;10(14):e34288. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34288. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39100497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Regulates Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA Levels.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 19;26(14):6942. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146942. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM. International variation. Oncogene 2004; 23: 6329–40. - PubMed
-
- Brechot C, Gozuacik D, Murakami Y, Paterlini‐Brechot P. Molecular bases for the development of hepatitis B virus (HBV)‐related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Semin Cancer Biol 2000; 10: 211–31. - PubMed
-
- Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J et al Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA 2006; 295: 65–73. - PubMed
-
- Guo X, Jin Y, Qian G, Tu H. Sequential accumulation of the mutations in core promoter of hepatitis B virus is associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in Qidong, China. J Hepatol 2008; 49: 718–25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

