Viewpoint matters: objective performance metrics for surgeon endoscope control during robot-assisted surgery
- PMID: 27422247
- PMCID: PMC5315708
- DOI: 10.1007/s00464-016-5090-8
Viewpoint matters: objective performance metrics for surgeon endoscope control during robot-assisted surgery
Abstract
Background: Effective visualization of the operative field is vital to surgical safety and education. However, additional metrics for visualization are needed to complement other common measures of surgeon proficiency, such as time or errors. Unlike other surgical modalities, robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery (RAMIS) enables data-driven feedback to trainees through measurement of camera adjustments. The purpose of this study was to validate and quantify the importance of novel camera metrics during RAMIS.
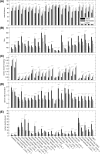
Methods: New (n = 18), intermediate (n = 8), and experienced (n = 13) surgeons completed 25 virtual reality simulation exercises on the da Vinci Surgical System. Three camera metrics were computed for all exercises and compared to conventional efficiency measures.
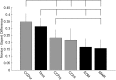
Results: Both camera metrics and efficiency metrics showed construct validity (p < 0.05) across most exercises (camera movement frequency 23/25, camera movement duration 22/25, camera movement interval 19/25, overall score 24/25, completion time 25/25). Camera metrics differentiated new and experienced surgeons across all tasks as well as efficiency metrics. Finally, camera metrics significantly (p < 0.05) correlated with completion time (camera movement frequency 21/25, camera movement duration 21/25, camera movement interval 20/25) and overall score (camera movement frequency 20/25, camera movement duration 19/25, camera movement interval 20/25) for most exercises.
Conclusions: We demonstrate construct validity of novel camera metrics and correlation between camera metrics and efficiency metrics across many simulation exercises. We believe camera metrics could be used to improve RAMIS proficiency-based curricula.
Keywords: Endoscope control; Performance metrics; Proficiency; Robot-assisted surgery; Surgeon training; Visualization.
Conflict of interest statement
A M. Jarc is a Senior Medical Research Scientist at Intuitive Surgical, Inc. M. Curet is a Senior Vice President and Chief Medical Officer at Intuitive Surgical, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Comparison of Robotic Simulation Performance on Basic Virtual Reality Skills: Simulator Subjective Versus Objective Assessment Tools.J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017 Nov-Dec;24(7):1184-1189. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2017.07.019. Epub 2017 Jul 27. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017. PMID: 28757439 Clinical Trial.
-
Face, content, and construct validity of four, inanimate training exercises using the da Vinci ® Si surgical system configured with Single-Site ™ instrumentation.Surg Endosc. 2015 Aug;29(8):2298-304. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3947-2. Epub 2014 Nov 1. Surg Endosc. 2015. PMID: 25361660
-
Examining validity evidence for a simulation-based assessment tool for basic robotic surgical skills.J Robot Surg. 2019 Feb;13(1):99-106. doi: 10.1007/s11701-018-0811-8. Epub 2018 May 14. J Robot Surg. 2019. PMID: 29761352
-
A review of training research and virtual reality simulators for the da Vinci surgical system.Teach Learn Med. 2015;27(1):12-26. doi: 10.1080/10401334.2014.979181. Teach Learn Med. 2015. PMID: 25584468 Review.
-
Towards standardized robotic surgery in gastrointestinal oncology.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2017 Nov;402(7):1003-1014. doi: 10.1007/s00423-017-1623-4. Epub 2017 Sep 27. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2017. PMID: 28956165 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Main Influencers of Surgical Efficiency and Variability Using Task-Level Objective Metrics: A Five-Year Robotic Sleeve Gastrectomy Case Series.Front Surg. 2022 May 2;9:756522. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.756522. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 35586509 Free PMC article.
-
Measures of performance and proficiency in robotic assisted surgery: a systematic review.J Robot Surg. 2024 Jan 13;18(1):16. doi: 10.1007/s11701-023-01756-y. J Robot Surg. 2024. PMID: 38217749
-
Development and validation of non-guided bladder-neck and neurovascular-bundle dissection modules of the RobotiX-Mentor® full-procedure robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy virtual reality simulation.Int J Med Robot. 2021 Apr;17(2):e2195. doi: 10.1002/rcs.2195. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Int J Med Robot. 2021. PMID: 33124140 Free PMC article.
-
Objective performance indicators versus GEARS: an opportunity for more accurate assessment of surgical skill.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024 Nov;19(11):2259-2267. doi: 10.1007/s11548-024-03248-2. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024. PMID: 39320413
-
Objective performance indicators during specific steps of robotic right colectomy can differentiate surgeon expertise.Surgery. 2024 Oct;176(4):1036-1043. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2024.06.040. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Surgery. 2024. PMID: 39025692
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

